Share
0
/5
(
0
)
Electronic trading has gone through many stages of development, and today it offers access to a complex system of capital markets where every second, tens of thousands of orders are to buy and sell an incredible variety of trading instruments, from Forex to crypto.
The process of handling market orders is complex and includes the work of many systems and mechanisms, the coordinated work of which ensures the fulfilment of the ultimate goal of the trading process — the fulfilment of orders. One such system is smart order routing.
This article will explain smart order routing systems and how they work. You will also learn what routing systems exist today and what applications they are used for.
Key Takeaways
Smart order routing is a system that automatically scans multiple markets to find the best, suitable order matches.
Such a system excels at securing favourable prices within time-sensitive windows.
SOR systems are especially effective in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies and certain FX pairings.
What is Smart Order Routing?
Smart order routing (SOR) is an automated technology used in financial markets to optimise the process of executing trades by finding the best possible conditions for an order.
It analyses multiple trading venues (exchanges, dark pools, liquidity providers, etc.) in real time to determine where to route an order to achieve the most favourable execution for a trader.
The goal is typically to maximise returns by securing the best price, minimising transaction costs, and reducing market impact.
SOR not only seeks the best price but also considers factors like order type, volume, and market conditions to determine the optimal execution strategy. It may break large orders into smaller portions, routing them to different venues to reduce price slippage and take advantage of available liquidity.
SOR systems continuously monitor market activity, adjusting their strategies as conditions change to ensure timely execution and compliance with market regulations. This automation helps both retail and institutional traders by enhancing efficiency, reducing the need for manual intervention, and improving overall trading outcomes in increasingly fragmented and complex markets.
[aa quote-global]
Fast Fact
Algorithmic trading incorporates SOR systems into its methodology, enabling developers to design automated strategies that can be executed within seconds.
[/aa]
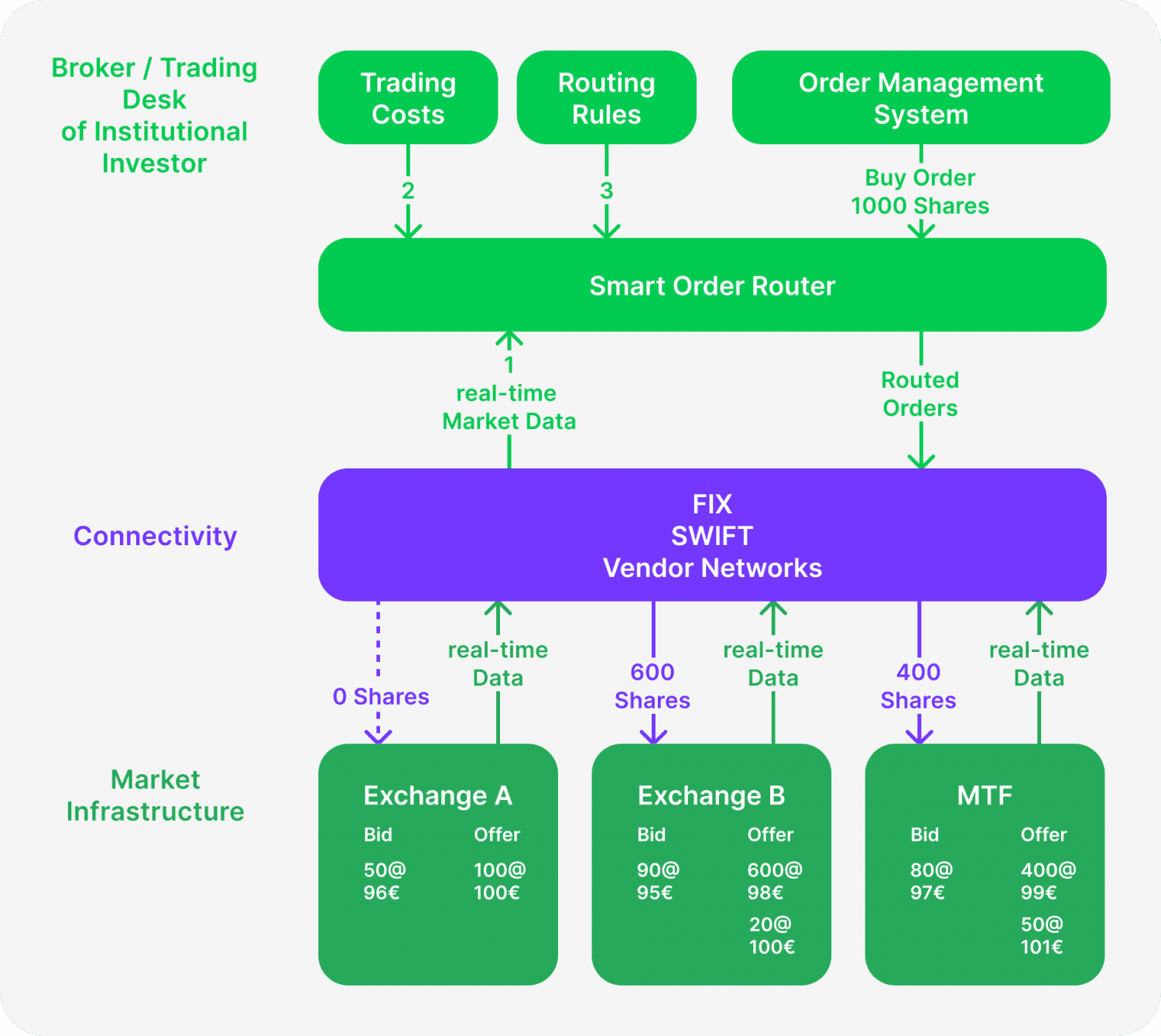
How Does Smart Order Routing Work? — Step-by-Step Operation Flow
Smart order routing is a complex set of processes occurring within the trading process, providing the best conditions for order execution in specific market conditions. Below is the list of stages included in such systems' standard workflow.
Receiving the Trade Order
The process begins when a trader (retail or institutional) submits an order through a trading platform or brokerage. This order could be a buy, sell, or other types such as limit, market, or stop order.
Market Data Analysis
Upon receiving the order, the smart order routing algorithms promptly process real-time market data from various trading venues, including stock exchanges, dark pools, alternative trading systems (ATS), and liquidity providers. It carefully assesses a range of factors, such as bid-ask spreads, available liquidity, trading volumes, and execution speed.
Order Routing Decision
After analysing the data, the SOR identifies the optimal venue or venues for order execution. Several key factors are considered, including finding the venue with the most competitive pricing, ensuring enough liquidity to complete the order, and considering the order size.
In the case of large orders, the system may divide the order across multiple venues to prevent slippage. Additionally, SOR evaluates the total cost of execution, considering any fees that different venues may charge.
Order Execution
The SOR system routes the order, or portions of it, to the chosen venues. For large or complex orders, it may split the order and execute parts simultaneously across multiple markets to optimise the overall execution.
Real-Time Monitoring and Adjustment
The SOR system monitors market conditions in real-time as the order is executed. If market conditions change (e.g., a better price or liquidity becomes available at another venue), smart order router software may adjust the routing strategy mid-trade to ensure the best outcome.
Order Completion and Reporting
Once the order is fully executed, the system provides feedback to the trader. The SOR will often compile post-trade analytics, showing details like the execution price, fees, and any slippage. This reporting helps assure transparency and allows traders to assess the effectiveness of the trade.
Regulatory Compliance
Throughout the process, the smart order routing system assures that the execution of the order complies with regulatory standards, such as best execution obligations under MiFID II (in Europe) or SEC rules (in the U.S.), ensuring that traders receive fair treatment.
Major Types of Smart Order Routes
Today, routing order systems are actively developing, and their varieties within the framework of trade practice number dozens. Here are the main ones:

Best Price Route
This routing strategy specialises in obtaining the most advantageous price for an order by surveying various trading venues and choosing the one with the most favourable bid or ask price. If the desired price has sufficient liquidity, the order is directed to that venue for execution.
This route benefits traders looking to secure the most competitive price for a buy order or the highest price for a sell order.
One of the key benefits of this routing strategy is that it maximises the likelihood of obtaining the best available price in the market.
Liquidity Seeking Route
Liquidity-seeking routes are designed to efficiently locate available liquidity in concealed and public trading venues, such as dark pools and alternative trading systems (ATS). This routing option is particularly valuable for executing substantial orders that must be completed without causing a significant impact on market prices.
This routing strategy is commonly utilised by institutional traders and hedge funds seeking to execute large orders while minimising the adverse effects of price slippage.
Cost-Sensitive Route
This routing system is designed to minimise transaction costs by considering the price and associated fees across various trading venues. It intelligently directs orders to venues with lower fees or cost structures, effectively managing cost efficiency while ensuring high-quality execution. This solution is particularly beneficial for traders keen on reducing overall transaction costs, including venue fees, clearing costs, and taxes.
Time-Sensitive Route
When utilising a time-sensitive route, the main priority is to prioritise speed. This method involves sending the order to the venue where it can be promptly executed, thereby minimising the potential for price fluctuations or delays.
This routing approach is particularly beneficial for high-frequency traders (HFT) or traders operating in volatile markets where prices experience rapid movements. By reducing execution latency, this approach enables orders to be fulfilled before market conditions change significantly, offering traders a competitive advantage in swiftly evolving markets.
Dark Pool Route
This trading strategy specifically targets liquidity in dark pools and confidential trading platforms where large volumes of shares are traded without affecting the public market. Here, the SOR is employed to pinpoint advantageous trading opportunities within dark pools, allowing for the execution of trades with minimal impact on the market.
This approach is particularly beneficial for institutional traders who must execute substantial orders discreetly without causing significant market movements.
Market Impact Minimisation Route
This strategy, known as a systematic internaliser, is intended to lessen the effect of substantial transactions on the market. SOR can divide the order into smaller segments and carry them out across various venues gradually to prevent impacting the price. It benefits traders handling significant block trades who aim to avoid noticeable price shifts that could affect the overall execution cost.
This approach aids in preserving price stability during the execution of large trades, thereby reducing slippage and shielding the order from unfavourable market responses.
Passive (Maker-Taker) Route
This routing strategy involves the placement of limit orders on trading venues that offer a rebate for adding liquidity to the order book (referred to as the “maker” side). The SOR system actively seeks out venues where a trader can participate as a liquidity provider, potentially leading to reduced costs or even the opportunity to earn a rebate.
This approach is particularly suitable for traders who are comfortable waiting for their orders to be filled at a specific price. By leveraging this strategy, traders can reduce their execution costs by earning rebates or paying lower fees in return for providing liquidity.
Aggressive (Taker) Route
When employing the aggressive route, a trader opts for immediate execution and is willing to incur higher fees to remove liquidity from the market. This type of order is directed to venues where it can be promptly executed, irrespective of price fluctuations.
This approach suits traders who require prompt order fulfilment and prioritises speed over execution costs. The main advantage of this strategy is the assurance of swift execution, especially in rapidly changing or volatile market conditions.
Internalisation Route
When following this route, the Smart Order Router (SOR) first looks for opportunities to execute the trade within the brokerage's internal order book, utilising internal liquidity, before directing it to external venues. This approach is designed to minimise external fees and exposure to market risks.
This routing strategy is particularly beneficial for brokers and market makers aiming to lower transaction expenses and enhance the speed of order execution for their clients.
Conditional Route
Routing based on predetermined conditions or triggers, such as price targets or volume thresholds, defines this type of routing. The order is routed and executed only when specific criteria are satisfied, enabling a more strategic approach to execution.
This method is particularly beneficial for traders employing algorithmic strategies that depend on precise market conditions. It offers traders greater control over execution, enabling them to patiently wait for ideal conditions before executing the order.
Real-World Applications of Smart Order Routing
SOR is an advanced algorithmic trading tool that optimises trade execution by dynamically routing orders to different exchanges, liquidity pools, and venues based on price, volume, and liquidity. Here are some real-world applications of SOR across various industries and trading environments:
Equity Markets
In equity markets, SOR helps institutional investors, asset managers, and hedge funds achieve the best possible price when buying or selling large blocks of stock. Depending on factors like order book depth, volume, and price fluctuations, it splits orders across exchanges, dark pools, and other venues.
SOR identifies real-time price differences between exchanges, allowing traders to exploit arbitrage opportunities across different venues and boost profits.
In markets like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or NASDAQ, SOR ensures that orders are executed simultaneously at the best bid or offer across multiple exchanges, reducing the chances of adverse price movement.
Cryptocurrency Trading
Cryptocurrency markets are fragmented across numerous exchanges, and liquidity can vary dramatically. SOR enables traders to access the best prices by simultaneously routing orders to multiple exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
In highly volatile cryptocurrency markets, SOR helps reduce slippage by dividing large orders into smaller ones and executing them across various liquidity pools, reducing the impact on the market price.
In DeFi, SOR routes trades across decentralised exchanges (DEXs) to ensure traders can access the best price. Platforms like 1inch use SOR to aggregate liquidity from multiple DEXs like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and Balancer.
Foreign Exchange (FX)
In FX markets, SOR helps institutions and corporate clients execute large currency orders by identifying the best trading venues, such as an electronic communication network (ECN) or an interbank platform.
When executing cross-border payments, SOR can find the optimal foreign exchange rates across multiple liquidity providers, ensuring that multinational corporations minimise transaction costs and exchange rate risk.
Hedge funds use SOR to access liquidity from multiple FX platforms, maximising efficiency in executing trades and reducing overall market impact, especially in illiquid currency pairs.
Fixed Income Markets
The bond market is highly fragmented, with different bonds traded across various platforms. SOR helps institutional traders locate the best prices and liquidity for corporate, municipal, and government bonds across multiple venues.
Fixed-income markets can have wider bid-ask spreads due to liquidity issues. SOR helps minimise spreads by routing orders to venues offering the best pricing, particularly for less liquid bonds.
Derivatives and Options Trading
Market-makers use SOR to optimise their order flows across various exchanges when trading derivatives or options, ensuring they can quote prices on multiple venues simultaneously.
SOR can also be used in volatility arbitrage strategies to ensure that options traders can efficiently buy or sell contracts at the best price across different exchanges.
When executing complex multi-leg option strategies (e.g., spreads, straddles), SOR ensures that each leg of the strategy is executed at the optimal venue to maximise profitability and minimise transaction costs.
Retail Trading Platforms
Retail trading platforms like Robinhood or TD Ameritrade use SOR to ensure users get the best execution prices for their trades. This is particularly important when liquidity is thin or market conditions are volatile.
SOR enables retail traders to buy fractional shares and execute smaller trades without incurring high costs, as the orders are routed to the most cost-effective venues.
Algorithmic Trading Firms
High-frequency trading (HFT) firms leverage SOR to execute microsecond trades, taking advantage of minor price discrepancies between exchanges. By optimising the routing of orders, these firms can generate profits from price differences in highly liquid markets.
For large orders, algorithmic trading firms use SOR to break orders into smaller pieces and execute them across multiple venues, minimising their market impact and reducing the risk of price movement.
Commodities Trading
In commodities markets like oil, metals, and agricultural products, SOR executes orders across global exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and Intercontinental Exchange (ICE). This ensures traders can access the best prices and liquidity across different time zones.
In energy trading, firms use SOR to optimise the routing of orders in fragmented markets where prices and liquidity can vary between exchanges.
Conclusion
Smart order routing is a transformative tool in modern trading that enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and optimises trade execution across diverse asset classes and fragmented markets. By dynamically routing orders to the most favourable venues, SOR ensures that institutional, retail, or algorithmic traders achieve the best possible prices while minimising slippage, market impact, and transaction costs.
As markets continue to evolve and trading environments become more complex, the role of SOR will remain crucial in enabling seamless, efficient, and competitive trade execution. Ultimately, SOR empowers traders to navigate liquidity fragmentation and price discrepancies, unlocking more opportunities in today's fast-paced financial landscape.
FAQ
What is smart order routing (SOR)?
SOR is an automated technology used in financial markets to optimise trade execution, analysing multiple trading venues in real-time to find the best price and liquidity, ensuring the most favourable execution for a trader's order.
How does SOR improve trade execution?
SOR helps improve execution by scanning different venues, identifying the best price, minimising transaction costs, and reducing slippage.
Which markets use smart order routing?
SOR is commonly used in equity markets but also applies to other asset classes like foreign exchange, commodities, and cryptocurrency trading.
How does SOR decide where to send an order?
SOR analyses several factors: price, available liquidity, venue speed (latency), and fees, determining the best venue or venues to execute the order and achieve the best overall result.
Read also