Share
0
/5
(
0
)
Trading on financial markets with hundreds of different assets and instruments is a continuous process that includes many components, such as analysis, decision-making and management, within which an individualised trading strategy is implemented.
Dealing with such a complex process of operating in the capital markets, each trader needs a specialised tool that helps to keep records and analyse all information about investment activities, which will serve as a basis for improving trading skills, risk and money management. Such a tool is called a trading journal.
This article will help you understand what a trading journal is and what components it consists of. You will also learn about the advantages of keeping such a journal and how to create your own by following simple steps.
Key Takeaways
The trading journal offers the possibility to work with trade information in a comprehensive way and to interpret it to improve trading efficiency.
A trading journal includes many elements, such as trade rationale, market conditions, trade details, analysis of risks and rewards, etc.
There are three main types of trading journals — notebook, spreadsheet, and special trading journal software.
What is a Trading Journal?
A trading journal is a detailed record-keeping tool that traders use to document their trades, strategies, and the thought processes behind each trading decision. It serves as a personal logbook, capturing crucial data and insights about trading activities such as entry and exit points, trade sizes, the rationale behind each trade, prevailing market conditions, and the emotions experienced during trades. By systematically recording these elements, traders can gain a clearer understanding of their performance and decision-making patterns.
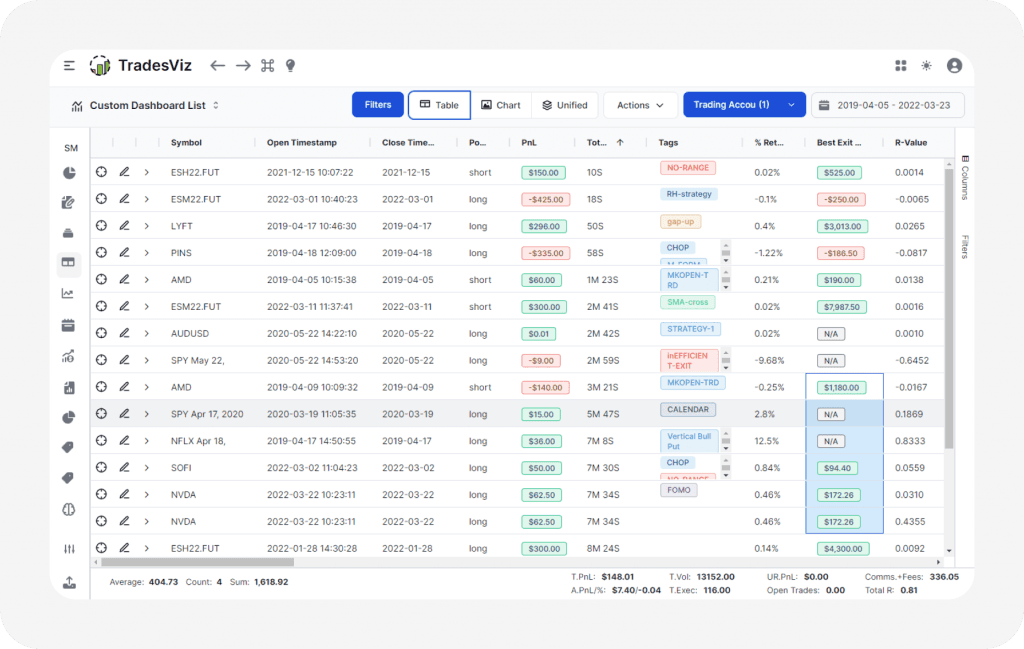
One of the primary purposes of a trading journal is performance tracking. It allows traders to evaluate their trading activities over time, identifying which strategies are yielding positive results and which are not. This detailed analysis enables traders to fine-tune their methods and approach, gradually improving their overall performance and profitability.
Also, the journal serves as a valuable resource for analysing patterns in trading behaviour and understanding the psychological factors that influence decision-making.
Other than that, a trading journal is an excellent tool for learning and improvement. By reviewing past trades, traders can identify mistakes and successes, gaining valuable insights that help refine their strategies.
It encourages reflection on each trade, making learning from past experiences easier and adjusting future actions accordingly. This process of reflection and learning can be truly enlightening for traders.
[aa quote-global]
Fast Fact
The trading journal is an integral component of many trader's room solutions.
[/aa]
Essential Components of a Trading Journal
A well-structured trading journal is an invaluable tool for traders looking to improve their strategies and performance. To maximise its effectiveness, it should include specific components that capture comprehensive details about each trade. Here are the fundamental components of a trading journal:
Trade Details
A trading journal captures the precise date and time of entry and exit for every trade executed. This practice is instrumental in evaluating how market conditions and temporal patterns influence trading outcomes.
It also helps to record the specific asset being traded, whether it be currency pairs, stocks, commodities, or cryptocurrencies, as this enables a comprehensive assessment of performance across various financial instruments. Additionally, it documents the size of each trade, including the number of units or lots involved, which is crucial for effectively analysing risk management and position-sizing strategies.
Entry and Exit Points
Recording the entry price is crucial because it shows the moment at which the trade began, enabling an evaluation of how well it fits your trading strategy. Likewise, tracking the exit price is important, representing the price at which the trade ended. This data is essential for calculating profit or loss and assessing the success of your exit strategy.
Trade Rationale
A free trading journal clarifies the rationale behind your trade entries. It is essential to articulate the reasons for entering a trade, which may include the technical or fundamental analyses that guided your choice. This could encompass various elements such as chart patterns, significant news developments, or particular indicators that played a role in your decision-making process.
Apart from that, it is crucial to outline your exit strategy within the journal. This should detail the specific conditions that will prompt you to close the trade, whether that be achieving a predetermined profit target, activating a stop-loss, or responding to shifts in market dynamics.
Market Conditions
This component helps to understand the prevailing market conditions during the transaction, including trends, levels of volatility, and pertinent economic news. Gaining insight into this context can help explain the factors that contributed to the success or failure of a trade.
Furthermore, if applicable, it highlights any significant economic reports or announcements that may have impacted the market dynamics during the trading period.
Risk and Reward Analysis
This component includes clearly defined stop-loss and take-profit levels, allowing you to establish a comprehensive risk management strategy by documenting the stop-loss and take-profit parameters established for every trade.
On the other hand, it computes and records the risk-reward ratio for each transaction, enabling you to assess whether your trades correspond with your intended risk profile.
Emotional State and Psychological Factors
This element encompasses emotions and encourages you to consider your emotional state throughout the trading process — were you experiencing confidence, anxiety, or uncertainty? Recording your emotions can assist in recognising psychological patterns that might impact your trading performance.
More importantly, it acknowledges any psychological triggers or biases that may have shaped your decision-making, including feelings like fear of missing out (FOMO) or excessive confidence.
Outcome and Performance Metrics
This category encompasses profit and loss metrics that are crucial for documenting the financial results of each trade, capturing both gross and net profit or loss. Such information is vital for assessing overall performance.
Performance metrics also include supplementary indicators like win rate, average profit per trade, and drawdown, which collectively offer a more comprehensive perspective on trading effectiveness.
Lessons Learned
This component facilitates the reflection and summarisation of essential insights gained from each trade, focusing on successful aspects, those that fell short, and areas for potential enhancement. This segment is vital for ongoing learning and the refinement of strategies. Further, as informed by reflections, it also pinpoints concrete actions or modifications to apply in upcoming trades.
Screenshots and Visuals
This component features charts that incorporate screenshots of the pertinent charts at the moments of entry and exit. Utilising visual aids can enhance comprehension of market conditions and assist in evaluating the trade setup.
Further, if relevant, it emphasises significant indicators or chart patterns that played a role in your trading decision.
What Advantages Does Maintaining a Trading Journal Offer?
Keeping a trading journal offers many benefits that can greatly enhance a trader's performance and overall market success by collecting, processing, analysing, organising, categorising and managing trading information as part of the investment activity. Here are some of the key benefits of working with professional trading journal software:
Performance Tracking and Analysis
A trading journal allows traders to track and review their trades over time systematically. By logging details such as entry and exit points, profit and loss, and trade sizes, traders can identify patterns in their performance. This helps them understand which strategies work well and which do not, enabling them to make data-driven adjustments to their trading approach.
Decision-Making
Documenting the rationale behind each trade helps traders reflect on their decision-making process. By reviewing past trades, traders can learn from both their successes and mistakes, leading to more informed and rational decisions in the future. This reflective practice can reduce the influence of emotions such as fear and greed, often leading to poor trading outcomes.
Discipline and Consistency
A trading journal helps reinforce discipline by encouraging traders to follow their pre-defined trading plans and strategies. By consistently recording their actions, traders become more accountable for their strategies, which promotes consistency in their trading behaviour and reduces impulsive, unplanned trades.
Learning and Development
Keeping a trading journal is an ongoing learning tool that provides valuable feedback. It allows traders to review their trades in detail and understand the impact of different market conditions on their strategies. This continuous learning process is crucial for adapting to changing market environments and improving trading skills over time.
Goal Setting and Accountability
A trading journal supports goal setting by allowing traders to set specific targets, such as achieving a certain profit level or reducing the number of losing trades. Regularly updating the journal with progress toward these goals fosters accountability and helps keep traders focused on their objectives.
Emotional Management
Trading can be emotionally challenging, with highs and lows that can influence decision-making. A trading journal can help traders recognise emotional patterns, such as trading out of boredom or revenge trading after a loss. By identifying these emotional triggers, traders can work on managing their emotions more effectively, leading to more rational and consistent trading behaviour.
Strategy Refinement
Traders can refine their approaches by keeping detailed records of each trade, including the specific market conditions and strategies. A trading journal provides insights into which strategies perform best under certain conditions, allowing for continuous optimisation and refinement of trading techniques.
Risk Management
A trading journal for the Forex market trading helps traders keep track of their risk exposure and adherence to risk management rules. By reviewing their trades, traders can identify instances where they deviated from their risk parameters, enabling them to correct such behaviours and better manage risk in the future.
Motivation and Progress Tracking
Regularly reviewing a trading journal allows traders to see their progress over time, which can be highly motivating. Observing improvements in performance or the achievement of goals can boost confidence and keep traders committed to their trading journey.
How to Create a Trading Journal
Being so important within the trading process, in particular, to ensure control and monitoring of the effectiveness of investment decisions, creating a trading journal is a question that is being asked by an increasing number of market participants who wish to succeed in the difficult world of electronic trading.

Here are the main aspects and nuances that need to be considered to create your first trading journal:
Step 1 — Choose Your Format
The first step involves selecting the format that suits your needs most effectively. You may opt for a trading journal spreadsheet, such as Excel or Google Sheets, which provides versatility and facilitates straightforward data analysis using formulas and charts.
Alternatively, dedicated software options like Edgewonk, TraderSync, or Tradervue offer tailored functionalities, including automatic data imports and performance analytics.
For those favouring a more traditional approach compared to an Excel trading journal, a manual notebook allows for a personalised touch, enabling traders to customise their records through handwriting.
Step 2 — Set Up the Essential Sections
This step involves a detailed analysis of all the components that should be contained in the best trading journal app. As mentioned above, these components include trade details, entry and exit points, market conditions, risk and Reward Analysis, emotional state, performance metrics, etc. All elements are interrelated and represent a system where each complements the other, ensuring the effectiveness of the trading journal.
Step 3 — Personalise to Fit Your Requirements
Adapt the journal to align with your trading approach: For day traders, emphasise finer details such as intraday trends, specific times, or particular triggers. For swing or long-term traders, concentrate on overarching market conditions, extended patterns, and the duration of trades.
Those engaged in algorithmic trading should incorporate technical aspects such as strategy specifications, code modifications, or algorithms' performance.
Step 4 — Maintain a Consistent Trade Log
Establishing consistency is essential; ensure you document your trades immediately after each transaction or trading day. Provide comprehensive details in your records, as the depth of information will enhance your analytical insights. Being candid about errors and emotional responses is essential, as these reflections are vital for your development as a trader.
Step 5 — Consistently Assess Your Journal
Daily or weekly assessments allow you to examine your recent trades, helping uncover patterns, errors, or potential areas for immediate improvement. On a monthly or quarterly basis, it is essential to analyse broader performance trends, the effectiveness of your strategies, and your compliance with risk management protocols.
Those utilising digital journals should use the integrated analytics features to evaluate their win rate, average returns, and other performance indicators.
Step 6 — Use Insights to Improve
In this step, leverage the insights gained from your journal to enhance and fine-tune your trading strategies. Adjusting your risk management practices to ensure they are in harmony with your performance metrics and the prevailing market conditions is essential.
Other than that, pay attention to emotional patterns that may influence your decision-making and take proactive measures to address any biases that could adversely affect your trading outcomes.
Step 7 — Keep It Simple and Evolve
Begin with a straightforward approach by initially focusing on fundamental information, gradually building upon it as you become more at ease. As your experience grows, add additional sections or details that enhance and refine your trading strategy.
Step 8 — Stay Disciplined
The effectiveness of your journal is directly linked to your dedication to regularly updating and reflecting on its contents. By committing to this practice, you enhance the overall value of the journal as a tool for your trading journey.
Further, the journal serves as a mechanism for accountability, ensuring you adhere to your established trading plan and guidelines. By utilising it in this manner, you reinforce your commitment to following the rules you have set for yourself, ultimately fostering a more disciplined approach to trading.
Conclusion
A trading journal is an essential tool for traders of all levels, offering a structured way to track trades, strategies, and emotional responses. By meticulously documenting each trade, traders can gain valuable insights into their performance, identify patterns, refine their strategies, and manage their emotions more effectively.
The key to a successful trading journal is consistency and honest reflection. Regularly reviewing your journal allows traders to learn from past mistakes, replicate successful strategies, and ultimately enhance your trading skills.
FAQ
What is a trading journal?
A trading journal is a detailed record-keeping tool that traders use to document their trades, strategies, and thought processes behind each decision.
Can I use a trading journal for all types of trading?
Yes, a trading journal is versatile and can be used for various types of trading, including Forex, stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. The key is to customise it to capture the specific details relevant to your trading style and markets.
What should I include in my trading journal?
Include trade details, strategy rationale, performance metrics, emotional reflections, and post-trade analysis.
How often should I update my trading journal?
Update it after every trade to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Can I use software for my trading journal?
Yes, many traders use specialised software or applications designed to track trades and analyse performance.
What are common mistakes to avoid while journaling?
Avoid skipping entries, being vague in your notes, and failing to review your journal regularly.
Read also





