Share
0
/5
(
0
)
With the widespread adoption of the internet and users submitting their personal information on every platform and service website, data risks and ID theft are becoming real issues. Which is what distributed digital identification tries to achieve!
While traditional data systems rely on centralised authorities to specify privacy concerns and policies, decentralised identity offers a revolutionary alternative: individuals can control their data.
Blockchain technology removes the need for middlemen and reduces the risks associated with centralised databases. But is that all? There’s more to this concept, so let’s explore it.
Concept Overview
Decentralised identity is a digital identification system allowing individuals to own, manage, and control their data and online footprint without relying on a central authority.
This approach enables users and organisations to create secure and private ID systems that are not shared with third parties and stored in identity wallets.
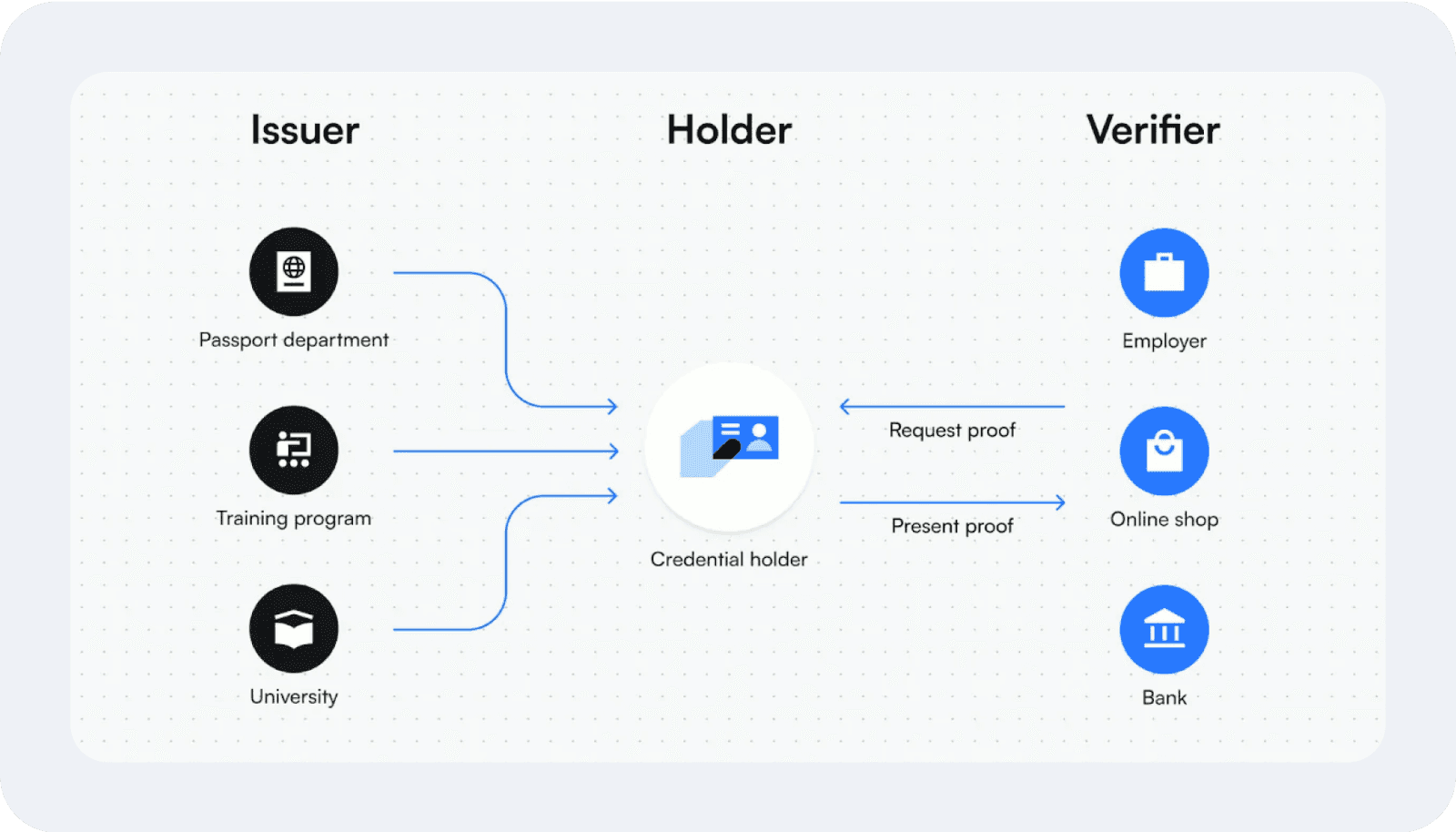
This information can be verifiable through decryption protocols, such as The Three-Party Model (Issuer, Holder, Verifier) or cryptographic proofs similar to those used by DeFi wallets’ private keys.
Users can practice freedom in sharing their data to selected destinations to ensure greater privacy and security. This approach enables trustless verification while reducing fraud and data breaches.
The Problem With Current Digital Identity
Traditional digital identity systems rely on centralised databases, which can be accessible to anybody sharing the system or due to server breaches. Personal information is stored by governments, corporations, or service providers, putting them at higher risk of exposure.
When you create an account with a bank, social media platform, or online service, your data is stored in their systems, creating several issues:
Security Risks – Centralised databases are the main targets for hackers, leading to breaches that can get hold of your data.
Lack of Privacy – Companies can collect, track, and share user data without consent, leading to identity misuse and less privacy.
Single Points of Failure – If the central server that stores your data gets hacked or shuts down, users lose access.
Limited User Control – Individuals must rely on third parties for verification and cannot control how their data is processed.
While centralised identity management is easier for less tech-savvy users, not requiring them to create or store any off-the-grid wallets or vaults, it comes at a significant privacy cost.
Decentralised identity solutions solve these issues by eliminating the need for a central authority and giving users control over their personal information.
How Does it Work?
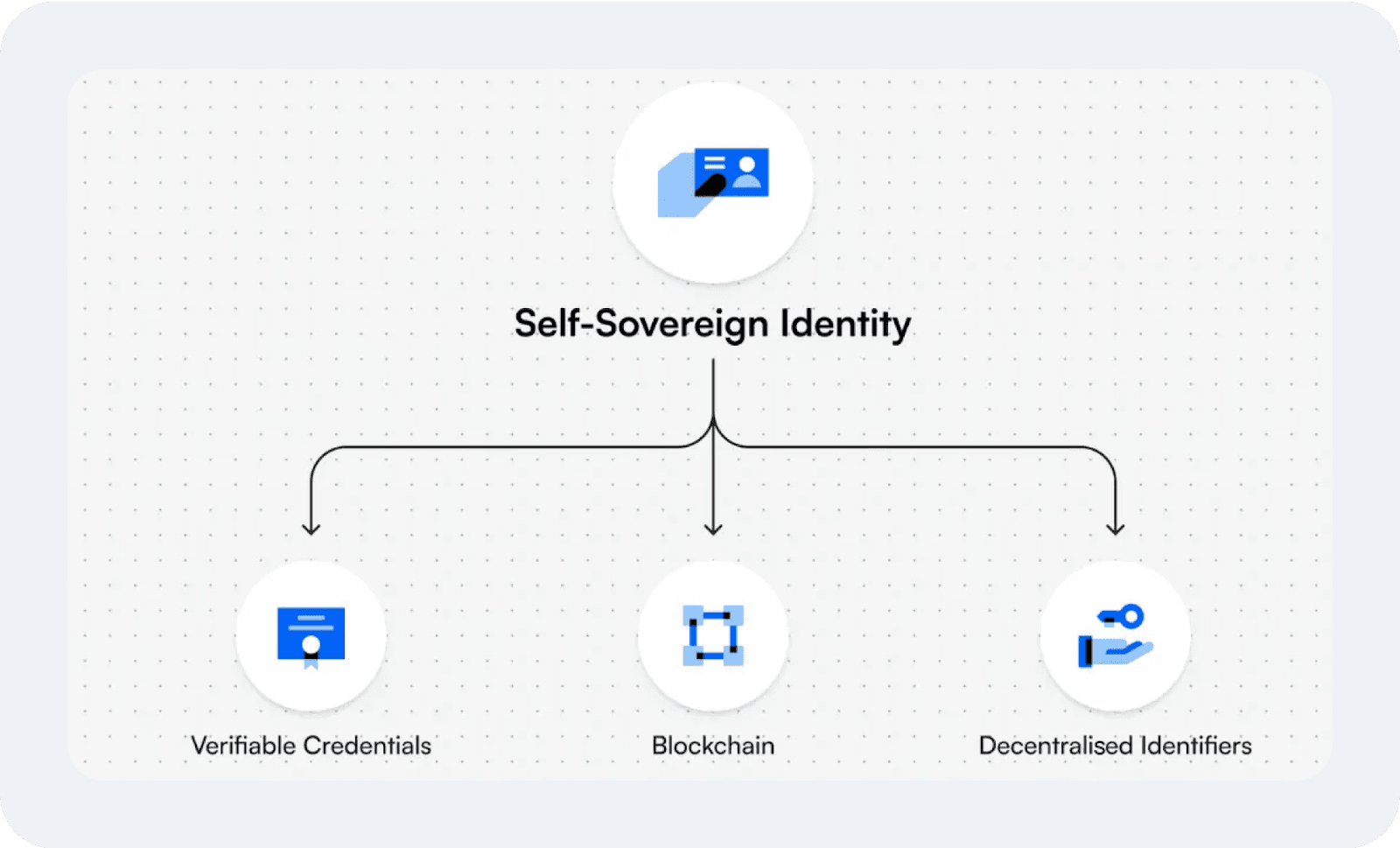
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) is the core principle of digital ID, referring to users having full control over their personal data instead of centralised storage and management.
Decentralised digital identity relies on distributed ledger technology (DLT) to ensure verifiable, tamper-proof, and secure identities. DLT distributes verification records across a network of nodes, making it more resistant to hacking and fraud.
The DLT provides a secure, manipulation-free environment to store and share personal data that can be verified without exposure. A decentralised identity system consists of the following components:
Blockchain: A distributed ledger shared across a network of computers that records data in a secure, tamper-resistant manner, making it highly resistant to alteration.
Decentralised ID wallets: A digital application that enables users to create decentralised identifiers and manage their credentials.
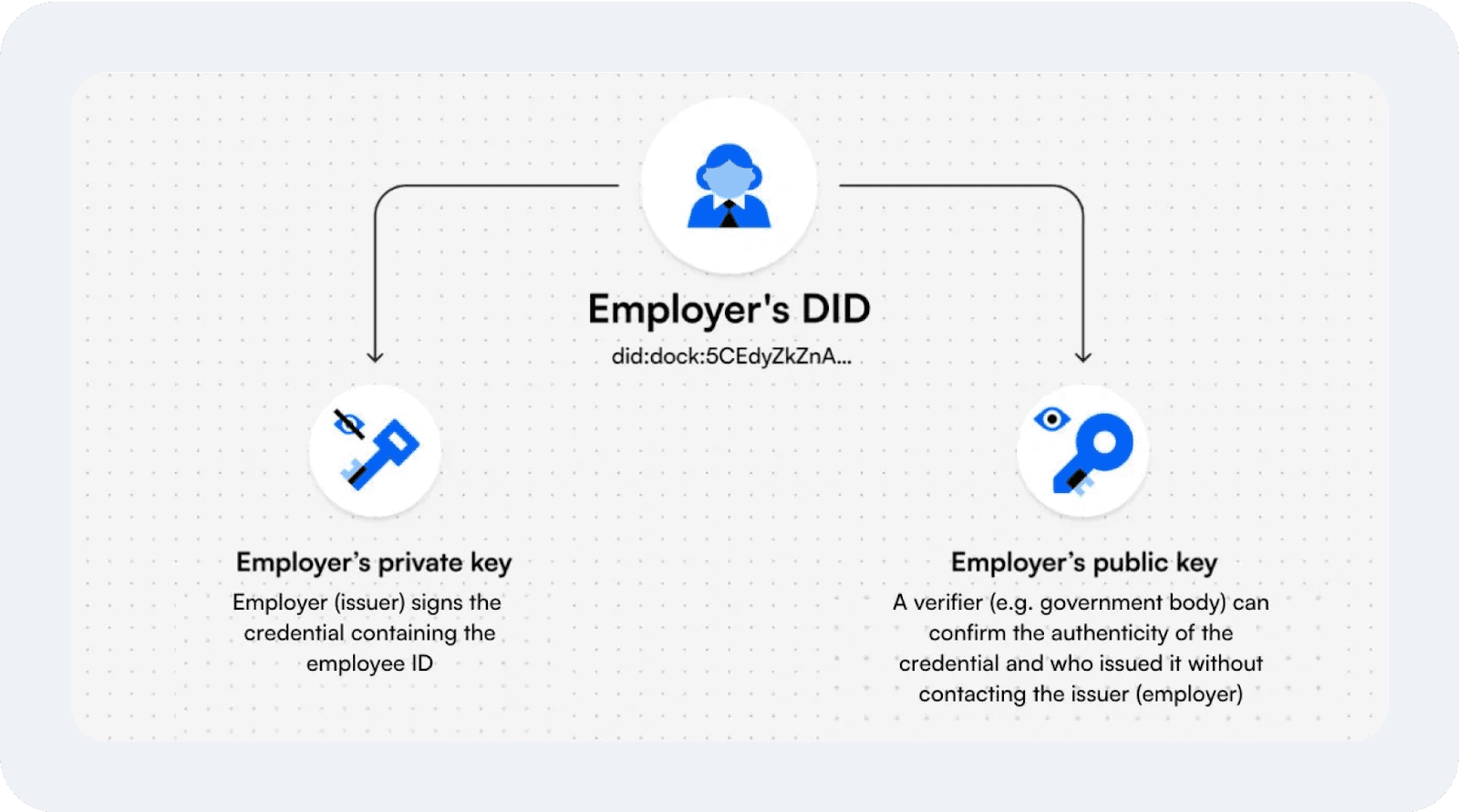
Decentralised identifiers: A unique identifier stored on the blockchain containing details such as the public key and verification details.
Verifiable credentials: A cryptographically secure version of traditional credentials that facilitates verification by organisations or other parties.
By removing intermediaries, DeFi identity management creates a secure, privacy-focused system where users manage their digital presence independently.
Key Elements
Decentralised identity management entails several core elements that ensure security, privacy, and trust in digital interactions.
Concepts like Decentralised Identifiers (DIDs), Verifiable Credentials (VCs), Blockchain and Distributed Ledgers, Identity Wallets, and the Verification Process power the user-centric ID model.
Decentralised Identifiers
DIDs are unique cryptographic identifiers individuals create and control without relying on a central registry. Unlike traditional IDs that governments or corporations issue, DIDs are stored on decentralised networks and contain all users’ digital footprints.
They enable verifiable, privacy-preserving authentication and can be used across multiple platforms without referring to a central authority.
Blockchain & Decentralised Ledgers
Blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) ensure the integrity of decentralised identification by providing a secure, tamper-proof system for recording DIDs.
While personal data is not stored on the blockchain, verification records and cryptographic proofs allow authentication without revealing other sensitive data. This prevents fraud and eliminates the need for central databases.
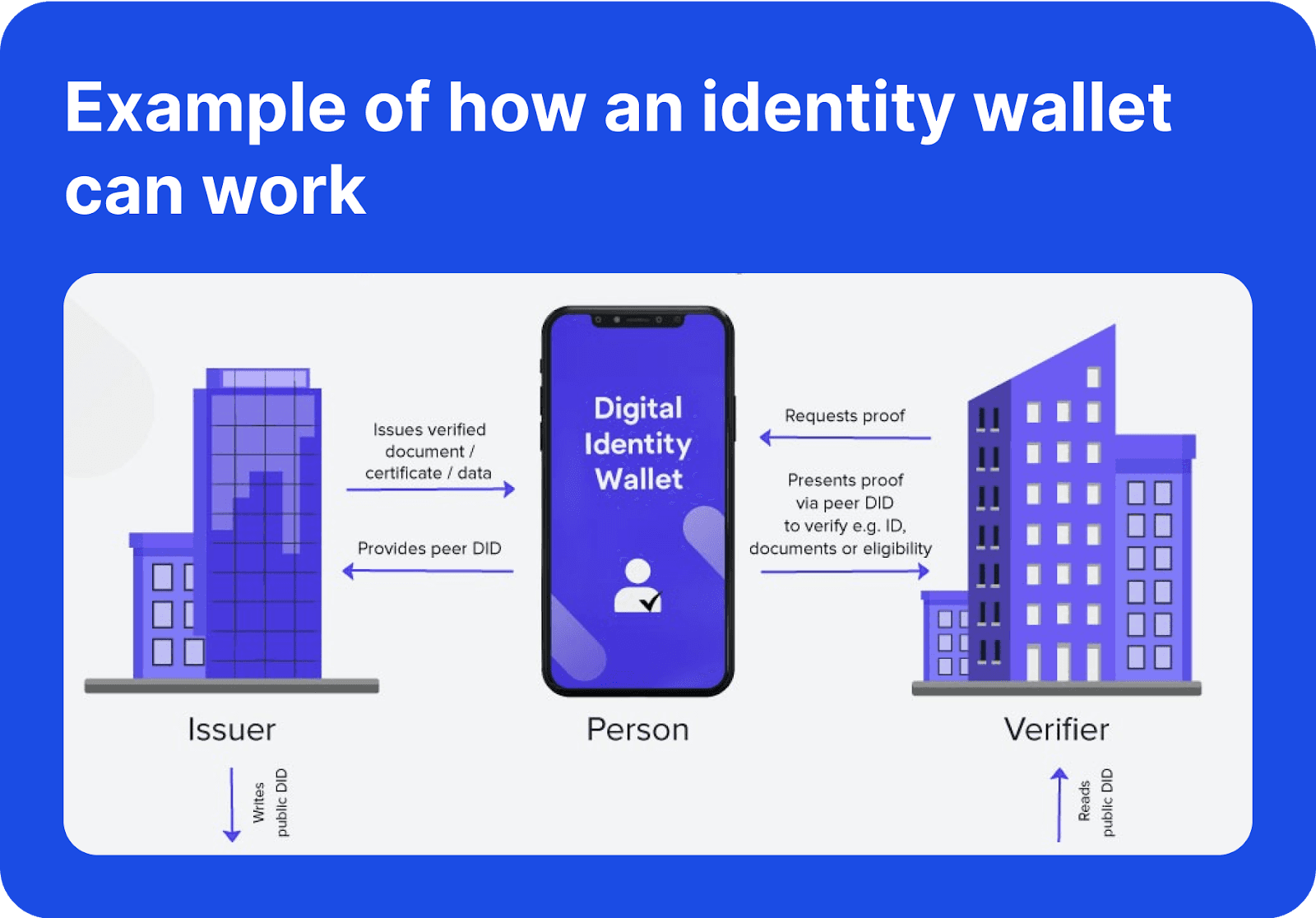
Identity Wallets
Identity wallets are secure applications that store and manage decentralised identifiers and verifiable credentials, like password vaults.
Users can control access to their credentials and share information with selected users or service providers. These wallets replace traditional authentication methods (like passwords), improving security while giving users full ownership of their digital presence.
Verifiable Credentials
VCs are digital certificates that prove attributes, like age or qualifications, without revealing unnecessary personal data.
These credentials are issued by trusted entities, such as governments or universities, and are cryptographically signed and stored in identity wallets. Users can present them for verification without exposing their entire identity, enhancing privacy and security.
Verification Process
The trustless verification process ensures reliability without exposing sensitive data. When a user shares a verifiable credential, qualification or certificate, the receiving party can check its authenticity using cryptographic proofs stored on the blockchain.
This allows secure, instant verification of digital credentials without requiring access to a central database or the original issuing authority.
Real-World Applications
While identity decentralisation and blockchain-secured data are exciting concepts, the pressing question is: What are their real-life use cases, and how do they benefit us? This question has different levels.
While it helps privacy-aware individuals keep their personal data off the Internet, decentralised identity companies allow organisations with enormous databases, money reserves, and servers to safeguard their components and prevent tampering.
They can be highly beneficial in the following sectors:
Finance & Banking – Enables secure Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures, reducing fraud and simplifying verification for financial institutions.
Healthcare: This option allows patients to control their medical records and share them securely with doctors or hospitals, ensuring privacy and reducing administrative overhead.
Education – Universities can issue verifiable digital diplomas, preventing credential fraud and enabling global qualification recognition without exposing names, genders, nationalities, etc.
Public Services: Governments can issue decentralised digital IDs for voting, tax filings, and social services, reducing the risk of data theft.
Enterprise & Workforce – Employees can use verified credentials for background checks and support job applications away from fraud or discrimination.
Any process or operation that requires relying on a centralised database or authorisation system can benefit from the DID systems to elevate trust and minimise fraud.
Benefits and Challenges
While concealed identity seems promising and plentiful, it can be a complicated concept to fathom. Moreover, it requires additional manual hassle and management, which not all users can perform. Let’s review the pros and cons.
Pros
Elevated Privacy & Security – No central data storage, reducing hacking risks and sensitive information exposure.
Superior User Control: Individuals can decide how and when to share their credentials and personal data.
Fraud Prevention: Reduces identity theft, fake accounts, and data breaches that harm individual users and organisations.
Interoperability: The concept is directly applicable across various platforms and user cases without referring to a single provider.
Faster Verification: Reduces bureaucracy in sectors like finance, healthcare, education, and governmental reporting.
Cons
Adoption Barriers: Many organisations still rely on centralised identity systems that all users and internal teams are aware of.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments may restrict decentralised identity frameworks to strengthen oversight.
User Responsibility: Losing private keys can mean losing access to one’s identity, leading to another single point of failure.
Integration Issues: Existing systems may struggle to adopt decentralised identity models and require expensive modification.
Conclusion
Decentralised identity is revolutionising digital identity management by giving individuals complete control over their data amidst the rising cyber threats and online exposure.
It enhances privacy, reduces fraud, improves service access, and ensures interactions between parties are built on trustless authentication.
Unlike traditional systems, which rely on central authorities and expose users to security risks, DID enables secure, private, and verifiable authentication.
While it is a premature, challenging concept, the growing adoption of DID by governments, businesses, and individuals signals a shift towards a more secure and user-centric digital world.
Read also