What is an Anti-Fraud System, and How Does it Work?

Globally, fraud is becoming a significant threat to enterprises of all sizes. Businesses must not only protect their own data and assets, but they must also keep an eye out for fraudulent actions from other sources.
An anti-fraud system can provide an extra layer of security against these hostile actors by monitoring real-time transactions and activity for discrepancies or anomalies that could indicate fraud.
In this blog post, we’ll define an anti-fraud system and explain how it works so you can see why it’s such an essential tool for assuring secure online transactions.
Key Takeaways
- Various fraud forms exist, including identity theft and money laundering, highlighting the necessity for effective anti-fraud systems.
- Anti-fraud systems use technology like fraud detection software and transaction monitoring to identify and prevent fraudulent activities, safeguarding businesses.
- Implementing Anti-fraud systems reduces financial fraud losses, ensures regulatory compliance, and boosts customer confidence.
- Key fraud prevention strategies include risk assessment, AML, KYC, KYT, and KYB processes.
Types of Financial Fraud in the Financial Field

When discussing an anti-fraud system, it is critical to understand the various types of fraud that firms must be aware of. Financial and identity fraud are the two prevalent examples of fraud.
Identity fraud usually entails taking someone’s personal information, such as their Social Security number or credit card information, and then using it fraudulently. This sort of fraud is typically committed through phishing emails or harmful software (malware) designed to steal data from victims’ computers.
Financial fraud encompasses any sort of fraudulent behaviour involving money, including credit card fraud, wire transfer fraud, money laundering schemes, and others.
Payment fraud is a frequent financial fraud involving making payments with stolen or forged credit card information. This can be accomplished by using stolen credit cards and making purchases without the cardholder’s knowledge or by creating counterfeit cards with false details.
Payment fraud is often difficult to detect since it requires considerable monitoring and analysis of transactions to find the anomalies that indicate this behaviour.
Money laundering is a type of financial crime that includes hiding the source of unlawfully obtained funds and making them appear legitimately earned.
Various strategies are used to accomplish this, such as creating fraudulent documents or moving money through multiple bank accounts and other financial institutions to conceal its source.
Money laundering strategies are frequently used to finance criminal operations and terrorist organisations, making such crimes particularly dangerous. It also poses a considerable risk to businesses because dealing with money obtained illegally can result in serious legal consequences.
Businesses must have robust fraud prevention solutions in place to prevent financial fraud. A system such as this may help protect a company from the various types of financial fraud outlined above and any other fraudulent acts. Let’s take a closer look at these systems.
Overview of Anti-Fraud Systems
Anti-fraud systems are designed to detect fraud, as well as prevent various fraud attacks. They are a set of procedures and technology that are used to detect, monitor, and report suspicious or potentially fraudulent activities within an organisation.
These technologies can help organisations decrease their exposure to financial losses associated with fraud by detecting and alerting staff to potential dangers early on.
Anti-fraud systems enable firms to take proactive measures against fraud and, if necessary, deliver evidence to regulatory authorities. Furthermore, anti-fraud systems can assist companies in meeting industry standards regulating the prevention of money laundering and other forms of financial crime.

The Benefits
Organisations benefit from anti-fraud technologies in a number of ways. First and foremost, they can assist in reducing the danger of financial losses due to fraud, as well as safeguard companies from potential legal repercussions.
Furthermore, anti-fraud technologies enable firms to take a proactive rather than reactive approach to fraud by offering early fraud detection and alerting personnel of any questionable activity. This makes it easier for businesses to respond quickly and efficiently when fraud is uncovered.
Another benefit of anti-fraud systems is that they can help organisations comply with industry regulations to prevent money laundering and other areas of financial crime. By having an effective system in place, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to preventing fraudulent activities, which can increase customer confidence and trust.
Furthermore, anti-fraud systems can provide further insight into an organisation’s financial transactions, which can help them tailor their processes and identify areas where they may be vulnerable to fraud.
Finally, anti-fraud systems also enable organisations to have visibility into the activities of their partners and vendors as well as their own operations. This can help ensure that all parties involved in a transaction are following proper protocols and regulations.
Additionally, it can help businesses protect themselves from any malicious activity carried out by third parties, thus reducing the risk of financial losses due to fraud or other criminal activity.
Overall, anti-fraud systems offer numerous benefits to organisations looking to protect themselves against fraudulent activities in the finance industry.
Components of Anti-Fraud Systems
The effectiveness of an anti-fraud system ultimately depends on how well it is implemented, monitored, and maintained. Organisations must have a thorough understanding of their specific needs to choose the right system for them.
The components of an anti-fraud system usually include fraud detection software, risk assessment software, transaction monitoring systems, data analysis tools, and more.
- Fraud detection software is designed to detect irregular transactions and activities that may indicate fraudulent behaviour. This can involve analysing customer data and identifying patterns that have the potential to signal fraud.
- Risk assessment software helps organisations determine the probability of an incident occurring, as well as assess any potential losses they may incur should it occur.
- Transaction monitoring systems allow businesses to monitor all of their accounts regularly and flag suspicious or out-of-the-ordinary activity.
- Data analysis tools provide insights into patterns of fraudulent behaviour and help identify areas where fraudsters are most likely to strike.
Additionally, identity authentication systems can be used to ensure customers are who they say they are by verifying various personal information.
These components can be used together or separately depending on the organisation’s individual requirements and budget constraints. With the help of these systems, businesses can protect themselves from financial fraud and other malicious activities.
In addition to the components of anti-fraud systems, organisations should be aware of the different fraud detection methods they can use to identify and prevent fraud. We will discuss some of the fraud detection methods in the following section of the article.
Fraud Detection Methods
Anti-fraud systems use various fraud detection methods to identify and prevent fraudulent activities. These methods include rules-based analysis, statistical analysis, anomaly detection, machine learning models, and more. In this section, we will discuss some common detection methods used in anti-fraud systems.
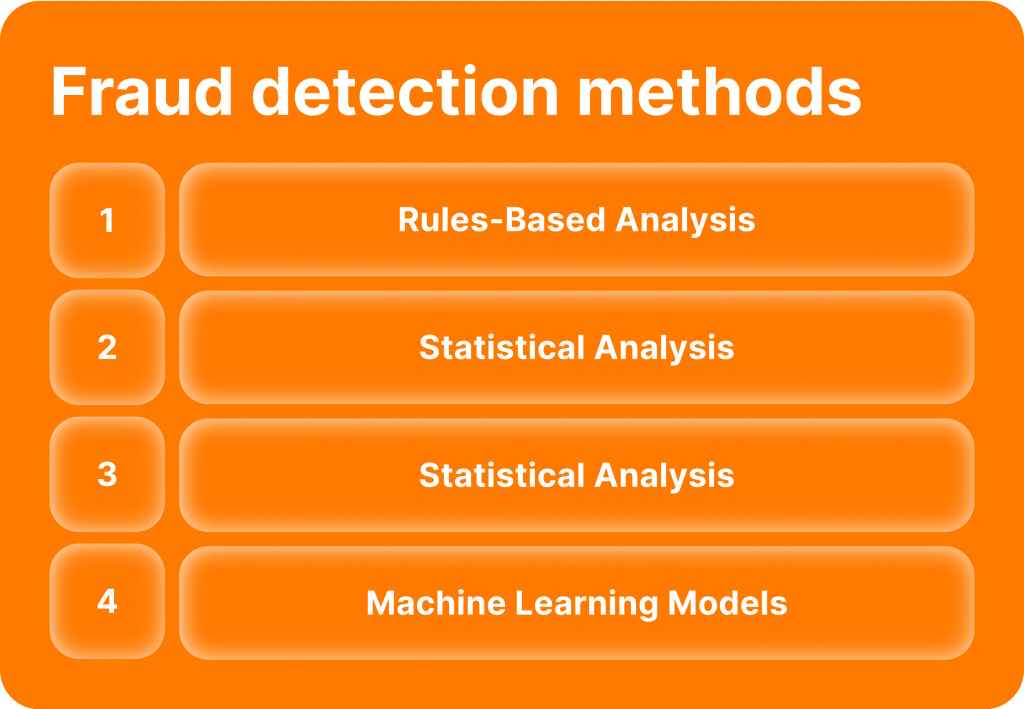
Rules-Based Analysis
This fraud detection method is based on predetermined parameters and thresholds set by the system administrator. When an activity or transaction falls outside these parameters, it triggers an alert that can be used to investigate further for any signs of fraud.
Statistical Analysis
This detection method analyses transactional data for patterns and anomalies that may signal fraudulent behaviour. Using sophisticated algorithms and mathematical models, statistical analysis can provide valuable insights into the likelihood of a transaction being fraudulent.
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly fraud detection is another method used in anti-fraud systems to identify suspicious transactions or activities that deviate from regular patterns. It typically uses machine learning models to analyse large amounts of data quickly and accurately to detect abnormalities.
Machine Learning Models
Machine learning models use AI technologies such as neural networks and deep learning algorithms to identify data patterns that could indicate fraud. These models are highly effective in quickly detecting irregularities that may otherwise go unnoticed.
These are just a few of the fraud detection methods used by anti-fraud systems. Each organisation needs to determine the best fraud detection method for its specific requirements to identify and prevent fraudulent activities effectively.
Fraud Prevention Systems

In addition to fraud detection methods, anti-fraud systems also employ various prevention measures that can help reduce the risk of fraudulent activities. This section will discuss some of the most common prevention strategies organisations use today.
Risk Assessment and Management
Risk assessment and management are essential components of any anti-fraud strategy. It entails evaluating a transaction’s risk based on various elements such as customer data, transaction trends, and external sources of information and then taking necessary steps to decrease or mitigate the risk.
Organisations must create strategies for risk management in addition to risk assessment. This includes establishing protocols for regularly monitoring transactions and executing procedures that ensure all transactions are appropriately validated before they are performed.
Also, organisations should have policies to deal with fraud quickly to reduce losses and protect their customers’ data.
AML
Anti Money Laundering (AML) is the process of detecting, preventing, and reporting suspicious transactions to prevent money laundering. AML regulations are designed to help organisations identify and report suspicious activities that could be indicative of money laundering or other financial crimes.
The critical components of a proper AML system include customer due diligence measures such as verifying customer identities and conducting background checks on customers; monitoring transactions for suspicious patterns or anomalies; setting up processes for flagging high-risk accounts; developing policies for dealing with sanctioned entities; and implementing procedures for reporting suspected violations to regulators.
Additionally, organisations can use analytics tools such as machine learning algorithms to detect suspicious activities more effectively by leveraging large amounts of data.
KYC
Know Your Customer (KYC) is the process of verifying a customer’s identity and other personal information. It helps organisations comply with legal requirements and protect themselves from financial fraud, money laundering, and other illegal activities.
The KYC process typically involves collecting and verifying customer data such as their name, address, date of birth, government-issued identification numbers, etc. This can be done either manually or by leveraging various digital solutions such as biometric authentication systems.
Apart from collecting the required information, businesses must also continually monitor customers’ accounts to detect any changes in behaviour or transactions that could signal suspicious activity. Additionally, organisations should have procedures for regularly reviewing and updating customer data to ensure it remains accurate and up to date.
Finally, organisations must also have practical systems for securely storing customer data and ensuring that it is only accessed by authorised personnel. This helps ensure that customer data remains secure and private, which is essential for maintaining customer trust.
KYT
Know Your Transaction (KYT) is a process of monitoring and verifying transactions to detect suspicious activity. It helps organisations comply with AML regulations, protect against financial fraud, and reduce the risk of money laundering.
KYT involves continuously tracking customer transactions for any irregularities or patterns that could indicate potential criminal activities such as money laundering or terrorist financing. This can be done either manually or by leveraging automated solutions such as anomaly detection algorithms.
Companies must also have adequate systems for reviewing flagged transactions and ensuring compliance with the relevant laws and regulations. Companies should also establish methods for routinely monitoring client accounts to detect any changes in behaviour or transactions that may indicate suspicious conduct.
KYB
Know Your Business (KYB) is the process of verifying a company’s identity and other business information. It helps organisations comply with relevant legal requirements, protect against financial fraud, and reduce the risk of money laundering.
The KYB process typically involves collecting and verifying data about a company, such as its ownership structure, corporate registration documents, banking details, etc.
Aside from gathering the necessary information, businesses must also have methods in place to spot any changes in their business activities that may indicate suspicious behaviour.
Finally, firms should consider integrating analytics tools to aid in the detection of possible fraudulent transactions. Overall, KYB helps ensure that companies are legitimate and can be trusted.
These four processes – KYC, KYT, KYB, and risk assessment and management – form the core of any effective anti-fraud system program. When implemented correctly, they help organisations meet their legal requirements for combating financial crime, protecting themselves from financial fraud, and reducing the risk of money laundering activities.
Regulatory Frameworks for Anti-Fraud Systems
The importance of having an effective anti-fraud system in place cannot be overstated. Regulatory frameworks ensure that organisations take the necessary steps to protect themselves from financial fraud and money laundering activities.
Some of the most critical regulatory frameworks for fraud prevention include:
#1 The International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) Principles – These principles set the minimum standards regulated firms must meet when developing, implementing, and operating an anti-fraud system program.
#2 The European Markets Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR): This regulation sets out rules on reporting transactions, risk management, clearing and settlement, organised trading facilities, central counterparties, and trade repositories. It also requires firms to develop protocols for detecting potential frauds or irregularities.
#3 The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Recommendations: These recommendations guide measures to detect and prevent money laundering activities. They require financial institutions to have effective systems in place for monitoring and identifying suspicious transactions.
$4 The U.S. Bank Secrecy Act (BSA): This act requires banks to maintain records of customer accounts, report suspicious activities to the appropriate authorities, and keep certain information confidential. It also includes provisions that require financial institutions to establish anti-fraud programs and procedures for reporting suspicious activity.
Apart from the above-mentioned regulatory frameworks, companies should also consider other relevant laws, regulations, and guidelines when developing an anti-fraud system program. Additionally, businesses should ensure that all processes are regularly monitored and updated as necessary to remain compliant with relevant legislation.
The Best Practices For Implementing Anti-Fraud Systems
An anti-fraud system is an important tool for organisations in the fight against financial fraud and money laundering. It requires careful planning and implementation to ensure that it meets all legal requirements while also being effective in identifying any suspicious activities.
To help businesses set up a successful anti-fraud system, here are some of the best practices to follow:
1. Develop Clear Policies and Procedures
Organisations should create clear policies and procedures that outline how the anti-fraud system works, who is responsible for its implementation, and what staff members must do when suspicious activity is detected.
2. Implement Regular Training Programs
It is essential that all employees be properly trained on the use of the anti-fraud system so that they can identify and report any suspicious activity. Training should include topics such as detecting and reporting fraud, money laundering, customer identification procedures, and so on.
3. Monitor Transactions Regularly
Organisations should set up a system to regularly monitor transactions to detect any signs of fraudulent activities or suspicious patterns. This could involve analysing customer information or monitoring for unusual or excessive transaction amounts.
4. Utilise Advanced Technology Solutions
The use of advanced technology solutions such as artificial intelligence (AI) can help organisations detect potential frauds more quickly and accurately than manual methods alone. AI-based solutions are becoming increasingly popular in the fight against financial crimes due to their ability to process large sets of data quickly and accurately.
5. Cooperate with Law Enforcement
Companies should cooperate with law enforcement agencies when suspicious activities are identified in order to ensure that any criminal activity is appropriately investigated and prosecuted.
Conclusion
Fraud prevention and fraud detection can be a daunting and complex process, but it is critical to the success of companies worldwide. A robust anti-fraud system can help identify threats at various levels, reduce risk, and make transactions more secure.
Organisations must constantly monitor for fraud, update their anti-fraud systems with effective methods, adhere to relevant regulatory standards, and educate their team members on potential vulnerabilities. These steps will provide the necessary protection from any fraud that may arise in the future.


