Share
0
/5
(
0
)
Imagine borrowing millions of dollars in crypto with no collateral, credit checks, or paperwork — all within seconds. Sounds impossible? Welcome to the world of crypto flash loans, a revolutionary DeFi innovation enabling traders to instantly execute high-frequency trades, liquidate positions, and optimise profits.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview for anyone interested in crypto flash loans, whether you are a DeFi trader seeking opportunities in flash loan arbitrage, a developer creating smart contract strategies, or simply someone eager to understand the mechanics behind them.
Key Takeaways
Flash loans provide instant liquidity with no collateral, making them lucrative for arbitrage, liquidations, and debt refinancing.
Platforms like Aave, Uniswap, and dYdX facilitate flash loans, allowing users to borrow, trade, and repay within the same transaction block.
Flash loans can be exploited in attacks, so DeFi platforms rely on decentralised oracles and security audits to mitigate risks.
What is a Crypto Flash Loan?
A crypto flash loan is an unsecured, immediate loan available solely within the decentralised finance space. In contrast to conventional loans that necessitate collateral or credit assessments, flash loans enable borrowers to obtain substantial liquidity without any initial capital, as long as they adhere to one essential requirement: the borrowed funds must be returned within the same blockchain transaction. Failure to meet this requirement reverses the entire transaction, protecting lenders from potential losses.
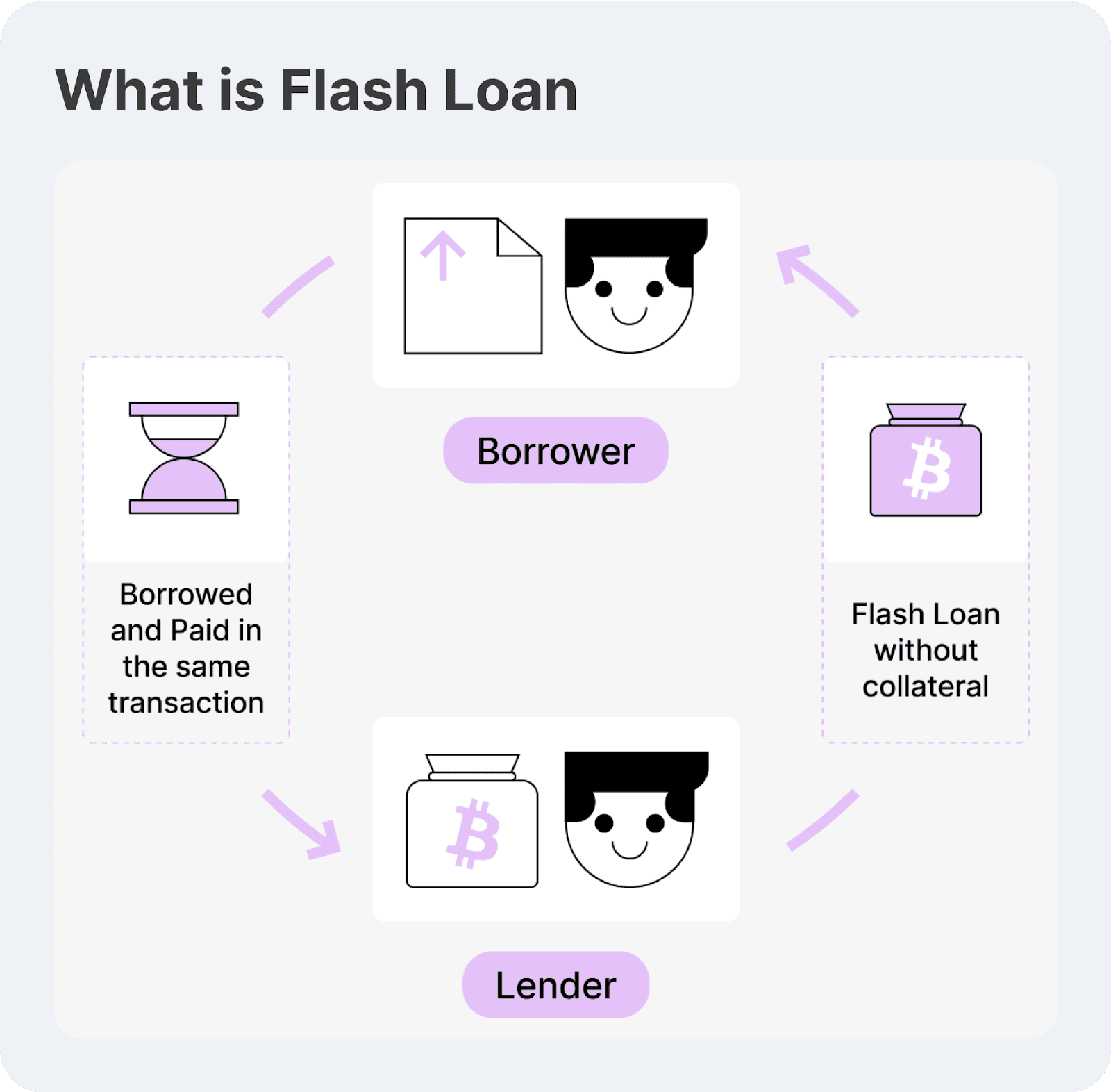
Flash loans are made possible through smart contracts and self-executing programs on blockchain networks like Ethereum. These contracts ensure that all steps of a flash loan — borrowing, executing a trade or operation, and repaying the loan — happen within a single atomic transaction.
The transaction is rolled back if any step fails, as if it never happened. This feature makes flash loans a powerful tool for traders, arbitrageurs, and DeFi developers looking to capitalise on price inefficiencies or optimise yield farming strategies.
[aa quote-global]
Fast Fact
Over $200 million in DeFi assets have been lost due to flash loan attacks, where hackers manipulate price oracles to drain liquidity pools.
[/aa]
How Do Flash Loans Work?
Flash loans operate based on atomic transactions, meaning that the entire transaction is settled correctly or none happens. When a borrower requests a flash loan, a smart contract temporarily transfers the requested funds to the borrower’s address.
The borrower then uses those funds to execute a predefined financial strategy — such as arbitrage trading, debt refinancing, or liquidation of undercollateralised positions.
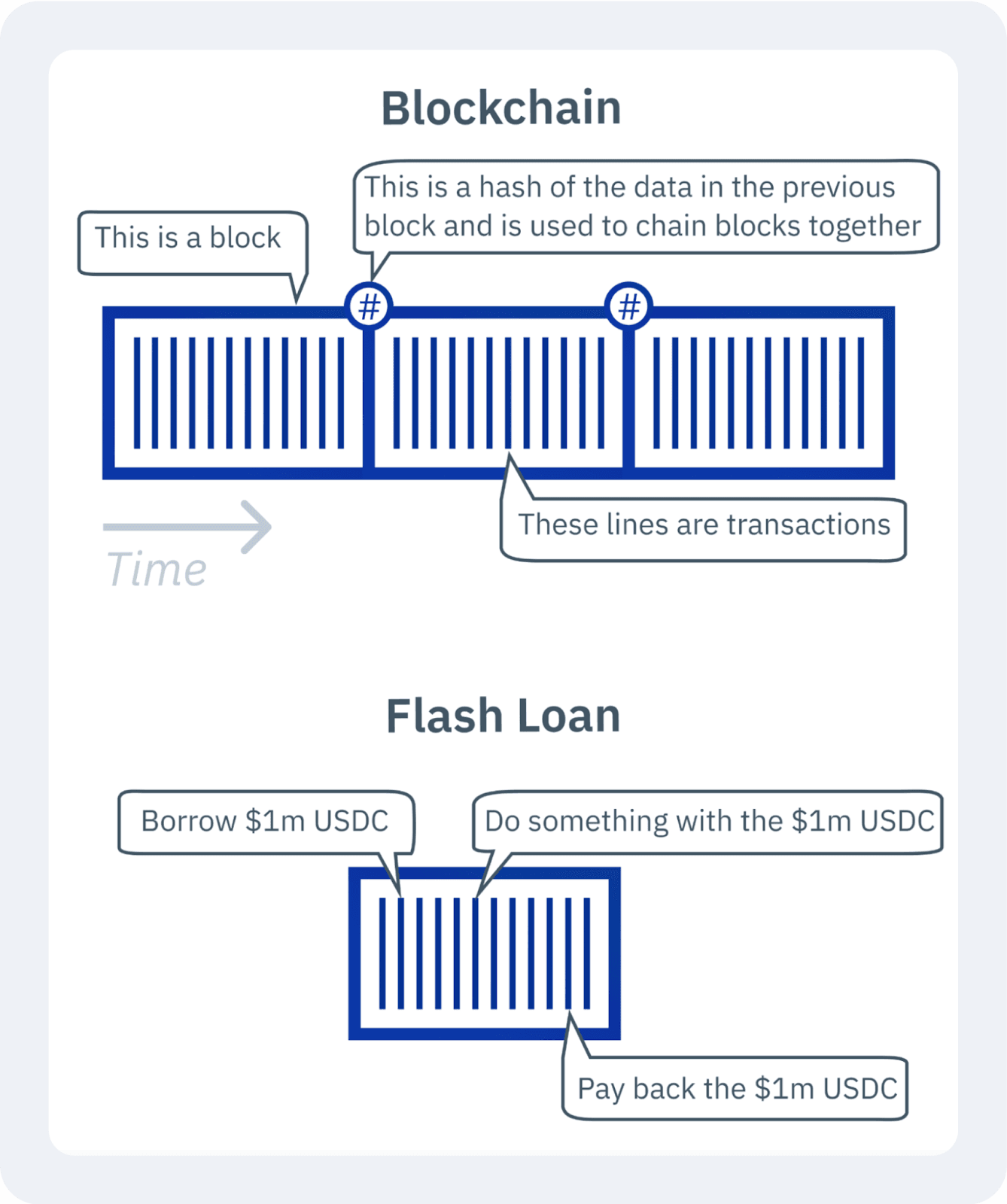
The transaction is validated and added to the blockchain if the borrower successfully executes their strategy and repays the loan within the same blockchain block.
However, if they fail to repay the loan, the smart contract cancels the transaction, ensuring no funds are permanently lost. This mechanism eliminates lender risk, so flash loans can be offered without collateral.
The Key Technologies Behind Flash Loans
Flash loans are a groundbreaking innovation in DeFi, allowing users to borrow large sums straightaway with no collateral. The loan is reimbursed within the same blockchain transaction. This mechanism is only possible due to several core blockchain technologies that enable flash loans to function securely and efficiently.
Here is a profound overview of the key technologies behind flash loans, explaining their role and significance in the ecosystem.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are the foundation of flash loans, operating as self-executing programs stored on a blockchain. These contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries by automating issuing, managing, and enforcing loan repayment conditions.
When a borrower requests a flash loan, a smart contract transfers the funds under strict conditions — requiring full repayment within the same blockchain transaction block. If the borrower fails to meet this requirement, the contract reverses the transaction as if the loan never occurred.
The security and efficiency of smart contracts make flash loans a risk-free lending mechanism. One of the best examples is Aave’s flash loan system, where a borrower gains access to liquidity, executes transactions and repays the loan plus fees in a single transaction.
If the repayment condition is met, the transaction is finalised. If not, the entire operation is cancelled, ensuring lenders’ funds remain secure.
Atomic Transactions
Atomic transactions ensure that every step within a flash loan process is executed as a single, inseparable unit. The entire process is automatically reversed if any part of the transaction fails — whether borrowing, executing trades, or repaying the loan. This guarantees that lenders do not lose funds and prevents partial execution failures, a common risk in traditional financial systems.
For traders leveraging arbitrage opportunities, atomic transactions are critical. Consider a scenario where a trader borrows 100 ETH via a flash loan, purchases tokens at a low price on one exchange, sells them at a higher price on another, and repays the loan — all within the same transaction block.
If, at any step, the market terms change and the arbitrage opportunity vanishes, the atomic transaction cancels everything, ensuring that no assets are lost and no debt remains.
Atomic transactions optimise high-frequency trading strategies by enabling instant execution without manual intervention. This automation allows traders to capitalise on short-lived market inefficiencies without exposing themselves to unnecessary risks.
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools are the primary funding source for flash loans, composed of assets provided by users who deposit their cryptocurrency into DeFi lending platforms. Unlike traditional banks that require loan collateral, liquidity pools provide unrestricted access to capital, enabling anyone with technical knowledge to borrow without upfront security.
DeFi protocols like Aave, dYdX, and Uniswap manage these pools, ensuring they remain fully liquid. Borrowers tap into the pools for flash loans, executing financial operations before returning the borrowed amount plus a small fee. Since the repayment occurs within the same transaction block, lenders’ funds are never at risk.
Liquidity providers benefit from these transactions as they earn passive income from fees collected on flash loans. This model strengthens the DeFi ecosystem by encouraging users to contribute funds, increasing the liquidity available for trading, arbitrage, and other financial strategies.
Decentralised Oracles
Oracles are external data providers that supply real-time market information to smart contracts, ensuring that transactions are executed based on accurate and tamper-proof data. In the context of flash loans, oracles play a crucial role in preventing market manipulation and enabling secure arbitrage opportunities.
Price feeds from decentralised oracles like Chainlink, Band Protocol, and API3 help ensure fair execution of arbitrage and liquidation strategies. Without reliable oracles, attackers could exploit price discrepancies, using flash loans to artificially manipulate asset values before executing profitable trades.
For example, a trader taking a flash loan for arbitrage on Aave relies on Chainlink’s price oracle to verify token values across exchanges. If an attacker attempts to alter asset prices maliciously, the oracle provides real-time pricing data from multiple sources, preventing any potential exploit.
Oracles also help ensure that liquidations within DeFi protocols occur fairly. When a borrower’s collateral value drops, an oracle verifies whether the drop is legitimate before triggering liquidation. This prevents wrongful liquidations based on manipulated prices and maintains stability in DeFi lending systems.
Use Cases for Flash Loans
Flash loans have revolutionised the DeFi ecosystem, providing traders, developers, and financial institutions with instant, unsecured loans that must be repaid within the same blockchain transaction. Since they require no collateral, flash loans have become a useful approach for arbitrage trading, liquidations, collateral swapping, and yield optimisation.
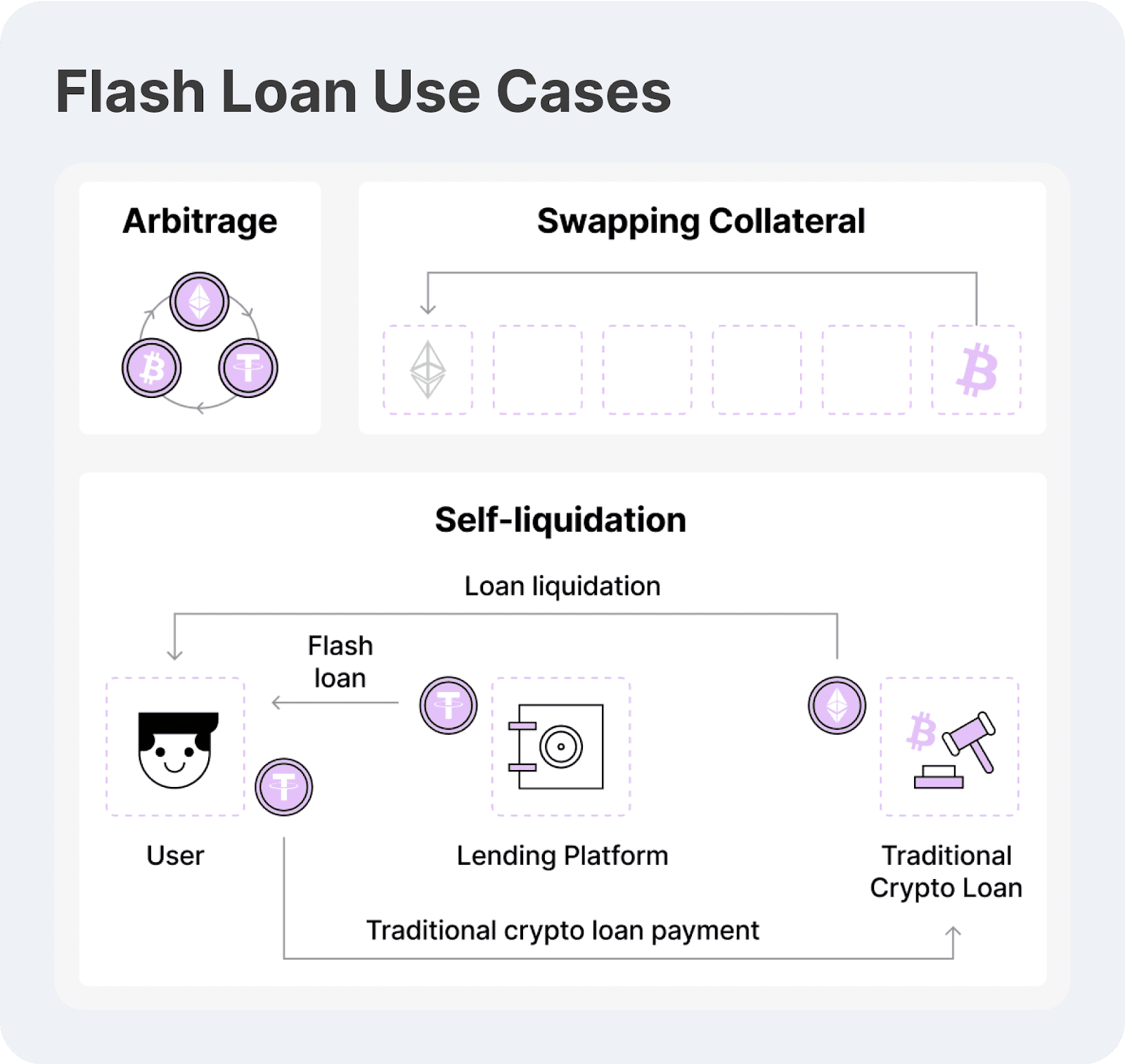
Below, we explore the most significant real-world use cases for flash loans and how they shape DeFi markets:
Arbitrage Trading
One of the most common applications of flash loans is arbitrage trading, where traders take advantage of price discrepancies between decentralised exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap, Sushiswap, and Curve Finance.
Since crypto assets can have slightly different prices across platforms, traders can borrow funds, buy an asset at a lower price on one exchange, and sell it for a higher price on another. This process is executed within a single transaction, ensuring profits while eliminating risk.
For example, if ETH trades at $3,000 on Uniswap but $3,050 on Sushiswap, a trader can take out a flash loan to borrow 100 ETH. They then buy ETH on Uniswap at $3,000 and immediately sell it on Sushiswap at $3,050. After repaying the loan within the same transaction, they keep the $5,000 profit (minus gas fees).
This method is highly effective because it allows traders to profit without requiring capital. Since arbitrage opportunities exist for only a few seconds, the speed and automation of flash loans make them ideal for high-frequency trading strategies.
Liquidating Under-Collateralised Loans
DeFi lending platforms like Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO require borrowers to maintain a minimum collateral ratio. If the value of a borrower’s collateral falls below the required threshold, the loan becomes under-collateralised and is subject to liquidation. Flash loans enable liquidators to step in, instantly repaying the borrower’s loan and seizing their collateral for a profit.
Consider a borrower with a $50,000 loan backed by $70,000 in ETH collateral. If the market crashes, liquidation is triggered by reducing the collateral’s value to $60,000. A liquidator can use a flash loan to borrow $50,000, repay the borrower’s loan, and receive the ETH collateral as a reward. They then sell the ETH for $60,000, repay the flash loan, and keep the remaining $10,000 profit (minus fees).
Flash loans make liquidation highly efficient by removing the need for upfront capital and ensuring lending platforms remain stable by preventing bad debt accumulation.
Collateral Swapping
Borrowers in DeFi often lock up collateral to secure loans, but if market tendencies shift, certain collateral types may become less favourable or at risk of liquidation. Flash loans allow borrowers to swap their collateral instantly without liquidating and manually reborrowing.
For an illustration, a borrower has a loan covered by ETH but expects ETH’s price to drop. Instead of waiting for liquidation, they take a flash loan in stablecoins (USDC or DAI), repay the ETH-backed loan, and immediately take out a new loan backed by the stablecoins, repaying the flash loan within the same transaction.
This process allows them to secure their loan with stable collateral, reducing liquidation risk. Flash loans provide a seamless way to switch collateral types while minimising transaction fees and improving loan stability.
Debt Refinancing
Interest rates vary across different DeFi lending platforms, and borrowers can reduce borrowing costs by shifting their loans to platforms with lower rates. Flash loans enable this process without requiring additional capital, allowing users to refinance debt in a single transaction.
Suppose a borrower has a $50,000 loan on Compound with a 10% interest rate, but Aave offers the same loan at a 5% interest rate. The borrower can take a flash loan to repay the Compound loan, freeing up their collateral. They then immediately take out a new loan on Aave at a lower rate and use it to repay the flash loan.
As a result, they maintain the same loan amount but with significantly reduced interest costs. Flash loans streamline debt refinancing by eliminating liquidation risks and enabling borrowers to optimise their loan positions efficiently.
Yield Farming and Liquidity Pool Optimisation
Yield farming involves shifting assets between DeFi platforms to maximise returns, as different protocols offer varying annual percentage yields (APYs) on staked assets. Flash loans allow farmers to move their liquidity instantly to platforms offering higher rewards, optimising their passive income.
For example, a yield farmer has $100,000 in liquidity staked on SushiSwap, earning a 10% APY. They notice that Uniswap offers 15% APY for the same liquidity pair. Using a flash loan, they withdraw their funds from SushiSwap, stake them on Uniswap, and repay the flash loan within the same transaction. This strategy enables them to increase earnings without withdrawing funds manually or paying additional fees. Flash loans make yield farming more capital-efficient by seamlessly allowing users to rebalance their assets across protocols.
How to Get a Flash Loan — A Step-by-Step Guide
Executing a flash loan involves choosing the right DeFi platform, setting up a compatible crypto wallet, understanding smart contract requirements, and deploying a transaction within a single blockchain block.
Below is a structured guide to obtaining and successfully executing a flash loan.
Step 1: Choose a DeFi Platform That Offers Flash Loans
Not all DeFi platforms provide flash loans, so selecting the right platform is essential. Some of the most well-known DeFi protocols offering flash loans include Aave, dYdX, and Uniswap. Each platform has requirements, fee structures, and smart contract functionalities.
Aave is one of the pioneers of flash loans, offering deep liquidity and a well-established framework. dYdX provides flash loans alongside margin trading, making it suitable for traders looking to execute complex financial methodologies.
Platforms like Uniswap and Balancer, primarily known for decentralised trading, allow liquidity pools to facilitate flash loan mechanisms. Before proceeding, users should review the platform's developer documentation and APIs to understand their specific requirements.
Step 2: Set Up a Web3 Wallet and Connect to the Platform
A Web3-compatible crypto wallet is necessary to interact with DeFi platforms. Popular choices include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Coinbase Wallet. Setting up a wallet involves creating an account, securing the seed phrase, and ensuring the wallet is funded with a small amount of ETH (Ethereum) or another blockchain-native token to cover gas fees.
Once the wallet is ready, users can connect it to their chosen DeFi platform. Most platforms provide a simple "Connect Wallet" button that enables interaction with their smart contracts. Assuring the wallet is properly set up and secured is crucial, as all transactions occur directly on the blockchain.
Step 3: Understand the Flash Loan Smart Contract Requirements
Flash loans operate through smart contracts, which automate the borrowing and repayment process. Since the entire loan transaction must be completed within a single block, failure to repay results in the transaction being reverted. This ensures that no funds are permanently lost or left unpaid.
Each DeFi protocol has specific rules for administering flash loans. The borrower must define the purpose of the loan within the smart contract, whether it's for arbitrage trading, debt refinancing, collateral swapping, or liquidations. If repayment is not completed within the same transaction, the blockchain nullifies the transaction, preventing any risk to the lender.
DeFi platforms offer developer documentation and Solidity-based smart contract examples for those with programming knowledge to help users create and execute flash loan requests. Understanding the technical requirements of these contracts is essential for ensuring a smooth transaction.
Step 4: Write or Use a Flash Loan Smart Contract
Executing a flash loan requires interacting with a smart contract that handles borrowing, utilising, and repaying funds. The process begins with creating a smart contract that interfaces with the chosen DeFi protocol. The contract should include logic to request the loan, execute a financial operation (such as arbitrage or liquidation), and ensure repayment within the same operation block.
Once the contract is written, it must call the flash loan function provided by the DeFi network protocol. The smart contract will then execute a predefined financial strategy, such as acquiring an asset at a lower price on one exchange and selling it for a higher price on another.
Upon completion of the operation, the contract repays the borrowed funds plus any required fees. If, for any reason, repayment does not occur, the blockchain reverses the transaction, ensuring that the borrowed funds are not permanently lost.
DeFi aggregators and third-party services provide user-friendly interfaces for users without coding expertise to execute flash loans without requiring in-depth programming knowledge. These platforms simplify the process but may charge additional fees.
Step 5: Execute the Flash Loan Transaction
Once the flash loan smart contract is ready, it must be deployed and executed. This uses Web3-based tools such as Remix Ethereum IDE, Hardhat, or Etherscan.
The process starts with deploying the contract to a blockchain network like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain (BSC), or Polygon. The next step is running the flash loan function, which triggers the borrowing mechanism. The operation must be carefully monitored to ensure that every step — from borrowing to repaying — is executed seamlessly within the same block.
Because Ethereum and other blockchain systems require gas fees for executing transactions, it is valuable to have enough ETH (or the native blockchain token) in the connected wallet to cover these costs. If gas fees are too high or the network is congested, transaction delays can lead to failed executions.
Step 6: Verify the Repayment and Monitor Transaction Status
After executing the flash loan transaction, verifying whether the repayment was successful is important. Users should check:
Whether the borrowed amount plus fees was repaid.
If the intended profit (if applicable) was transferred to their wallet.
Whether the transaction was successful or reverted due to a failure in execution.
Blockchain explorers like Etherscan (Ethereum) or BscScan (Binance Smart Chain) allow users to track transaction status by entering their wallet address. Users can troubleshoot the issue if the transaction fails by analysing smart contract logs or debugging execution steps.
Alternative Method — Using Flash Loan Services Without Coding
For those who lack technical knowledge, flash loan bots and third-party DeFi tools provide an easier way to access flash loans without writing custom smart contracts. These services offer pre-built flash loan processing functions, making it possible to:
Perform arbitrage trades without programming knowledge.
Liquidate under-collateralised loans using automated tools.
Swap collateral or refinance debt through simple UI-based interactions.
While these platforms make flash loans more accessible, they often charge additional fees and may pose security risks if not properly audited.
Final Remarks
Crypto flash loans have transformed decentralised finance, unlocking instant liquidity and limitless trading avenues. From arbitrage trading to debt restructuring and collateral swapping, flash loans empower users to maximise DeFi potential with zero upfront capital.
As the technology evolves, responsible usage, smart contract audits, and risk management will determine whether flash loans remain a powerful tool for traders or a double-edged sword for DeFi protocols from the future perspective.
FAQ
What is a crypto flash loan?
A flash loan is an unsecured, instant DeFi loan that must be borrowed and repaid within the same blockchain transaction.
How can I use flash loans for arbitrage?
Traders borrow funds via a flash loan, buy an asset on one exchange at a lower price, sell it on another for a profit, and repay the loan—all in one transaction.
Are flash loans risky?
For borrowers, flash loans are low-risk as they require no collateral. However, DeFi platforms are vulnerable to flash loan attacks, where exploits manipulate price oracles.
Which platforms offer flash loans?
Leading crypto flash loan providers include Aave, dYdX, and Uniswap, allowing users to borrow and execute trades instantly.
How can I get a flash loan without coding?
Non-developers can use flash loan bots and DeFi aggregators, which provide automated interfaces to execute flash loans for arbitrage, liquidations, and debt refinancing.
Read also




