Share
0
/5
(
0
)
Brokers need to understand and consider multiple details before they start operating. Choosing the operating model is the turning point, and these models are essential in FX trading. They decide how brokers manage risks and handle client orders. Every participant must be familiar with comparing two main concepts: the A Book broker vs B Book broker models.
By sending client orders straight to interbank market liquidity providers, an A-Book broker ensures transparency and keeps conflicts of interest at bay. A B-Book broker, on the other hand, profits when traders lose money by taking the other side in client trades.
This article compares the broker business model. It examines how they operate, their advantages, dangers, and effects on the trade environment. Thanks to these models, brokers may select the best strategy for their business, and traders can choose knowledgeable Forex brokers.
Key Takeaways
A-Book promotes transparency by transferring client orders straight to liquidity providers and averting conflicts of interest.
While B-Book may provide fixed spreads and speedier execution, it functions as a market maker and profits from its clients' losses.
Both hybrid models use both strategies to control risk and offer fair trading conditions.
What is an A-Book Broker?
An A-Book broker conducts business by sending customer orders to external liquidity providers in the interbank. This ensures that deals are carried out at competitive prices and that the broker does not profit from the trades. An NDD broker is another name for this type of broker model.
A-Book brokers get money via spreads and commissions. Spreads are the gap between the ask and bid prices, whereas commissions are fees assessed for each deal. Since the broker gains from higher trading volume rather than client losses, this revenue model balances the interests of the traders and the broker.
A-Book brokers have several advantages for traders. The broker cannot profit from traders' losses without conflict of interest. This model also offers increased transparency because trader orders are handled in the real market, which reflects actual market conditions. Additionally, because they have access to a large liquidity pool, A-Book brokers can provide superior trading conditions, like faster execution and tighter spreads.
Let’s now separate and highlight the critical characteristics of A Book Forex broker:
Direct communication with foreign exchange market liquidity sources.
Generating income via spreads and commissions.
No conflict of interest with the trades made by clients.
Better trading conditions and increased transparency for traders.
Access to the outside market for transaction execution will guarantee competitive pricing and lessen the impact of market volatility.
A-Book brokers are essential to the forex market because they provide retail traders with a fair environment. Their business strategy is centred on balancing the broker's and traders' profits to encourage profitable trading.
B Book Broker Meaning and Operation
In the B-Book model, the broker acts as a forex market maker and serves as the counterparty in a trade that a client makes. The broker loses if the client wins, and vice versa. This may lead to a conflict because the broker stands to gain financially from clients' losses.
Profits from client losses, spreads, and trade commissions are the three primary sources of income for B-Book brokers. This income model can be pretty lucrative for the broker, particularly during high market volatility when traders are more likely to experience losses.
The B-Book approach has advantages and disadvantages for traders. The main concern is the fundamental conflict of interest arising from the broker's financial interests directly opposing the trader's. On the other hand, B-Book brokers frequently provide fixed spreads and faster trade execution, which might be helpful in specific financial markets.
Critical characteristics of B Book Forex broker include:
Serving as the platform's counterparty for trades made by clients.
Making money off of commissions, spreads, and client losses.
Profiting off the losses of clients could create a conflict of interest.
More rapid trade execution and frequently set spreads.
Functioning without reference to outside liquidity providers or the outside market.
Forex B Book broker is an essential entity with varying benefits and risks compared to A-Book brokers. Thanks to their business model, they can offer particular kinds of traders and forex trading methods more control over pricing and execution.
[aa quote-global]
Fast Fact
According to some loose estimates, up to 95% of all FX/CFD brokers are considered B Book brokers, making it difficult for A Book model to compete.
[/aa]
Difference Between A Book and B Book Broker
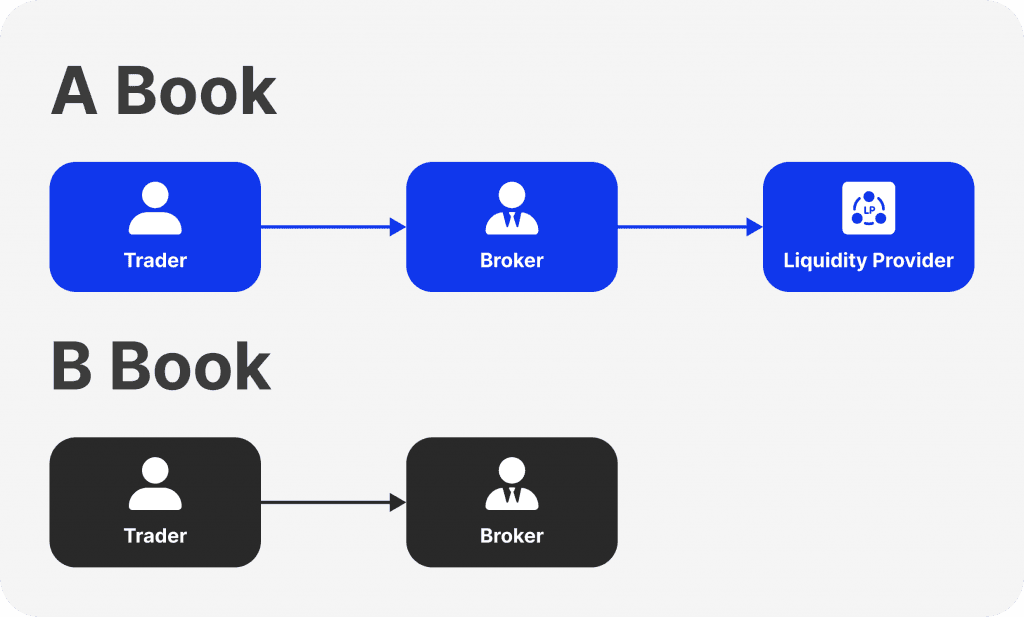
These models process client trades and conduct business differently. A-Book brokers usually submit client orders directly to liquidity providers to ensure transparency and possibly improved trading conditions for traders. However, because commissions and spreads are included in this arrangement, clients might pay higher prices.
On the other hand, B-Book brokers take a different view on customer trades, which may result in conflicts of interest. Although a B Book trading platform might provide reduced trading costs and quicker trade execution, price manipulation and information leakage can occur.
Every model has benefits and drawbacks. While B-Book brokers might provide quicker trade execution and reduced trading fees, A-Book brokers are preferred for their transparency and superior trading conditions. When selecting one of these models, traders should consider their trading objectives and preferences.
The Hybrid Model: Combining Both Approaches
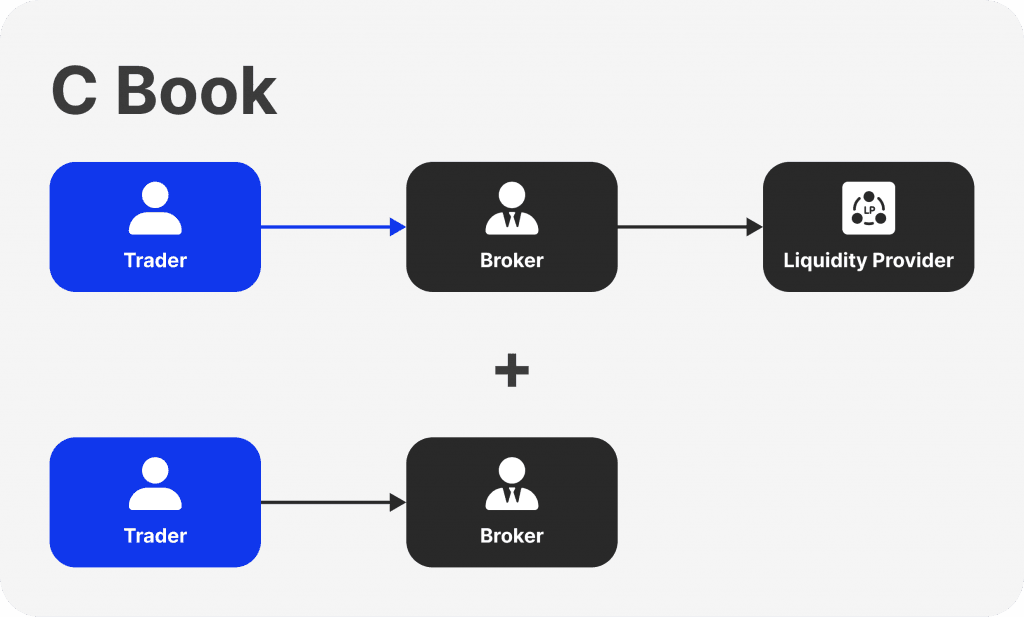
The hybrid broker model—called the C-Book—efficiently controls risk by combining aspects of both techniques. Under this strategy, brokers divide up client deals according to risk profiles. High-risk trades are handled internally (B-Book), while low-risk trades are routed to liquidity providers (A-Book).
Using this technique, brokers can profit from the advantages of both models. By forwarding low-risk deals to liquidity providers, they can guarantee transparency and improved client trading conditions. However, internal risk management of high-risk deals can assist brokers in reducing dangers and even boosting earnings.
However, the hybrid concept does have some difficulties. Accurate trade classification requires brokers to have sophisticated risk management systems, and keeping two different trading Books can further add to the operational complexity.
The hybrid approach is appropriate for brokers who want to balance risk and profit. It is frequently applied when there is significant market volatility or clients have different risk profiles.
Which Model Should Your Brokerage Choose?
There are various elements to consider when selecting. These characteristics can have an impact on both the performance of your firm and regulatory compliance. Here are some essential things to think about:
1. Regulatory Environment
The regulations in your jurisdiction may significantly impact your choice of broker model. A-Book, B-Book, or hybrid model criteria or limitations may be specific to certain regulators. Make sure the model you've selected complies with local laws.
2. Target Market
Your choices may also be influenced by your target market and clients' preferences. While some traders feel more at ease with B-Book brokers' potentially faster execution and cheaper trading expenses, others prefer the transparency and superior trading conditions provided by A-Book brokers.
3. Business Ambitions
Consider your business's long-term objectives and ambitions. If risk control and transparency are your top priorities, an A-Book format would be more appropriate. Conversely, a B-Book approach can be more suitable if your primary objective is to maximise profitability.
Some Suggestions
Newly established brokerages must consider a model that balances risk management and competitive trading conditions. One approach is to start with a model like the A-Book model, which provides transparency and equitable trading circumstances. Establishing a good reputation in the industry and fostering client trust are two benefits of this strategy.
On the other hand, well-established brokerages ought to review their current strategy regularly to ensure it still fits their changing objectives. Moving to a new model—like the B-Book model—may have benefits like increased price control and possibly improved profitability. However, the influence on client relationships and the entire business strategy should be carefully considered before making this decision.
Last Remarks
To summarise everything we've discussed, it is critical to comprehend broker models in the Forex trading world. A-Book brokers provide better conditions and transparency, while the B-Book model offers potentially higher profitability. The style and objectives will determine which one to use. Both new and veteran brokerages can find a middle ground with hybrid models. Choosing the right one is critical to success.
Read also





