Guide to Creating a Ticketing System

Today, any business has a base of different types of customers who use its products and services on a daily basis. In the process of cooperation, customers often have questions and difficulties, the solution of which is entrusted to the customer support service.
Until recently, such services had to manually receive, process, and resolve issues related to difficulties using one or another product. However, thanks to the IT sphere, a system was born that helps to automate and optimise all routine tasks based on tickets.
This article will help you understand a technical support ticketing system and its functionality. It will also explain the main reasons why you should create and implement such a system and provide a step-by-step guide on how to do it.
Key Takeaways
- The ticketing system is an important link in the interaction between the customer assistance team and the company’s clients, providing a means of solving their questions and problems.
- The ticketing system optimises and automates the processes of receiving, sorting, ranking, prioritising, processing, and solving tickets received from customers.
- A ticketing system is a component of any CRM system, which is part of a complex solution for lead generation and working with both new and existing customers.
What Is a Ticketing System?
A ticketing system is a software application or platform organisations use to manage and monitor customer inquiries, issues, and requests. It acts as a centralised hub, allowing for collecting, categorising, and resolving customer tickets or support tickets. This tool enables businesses to handle customer assistance requests promptly and effectively and provides a streamlined process for addressing customer concerns.
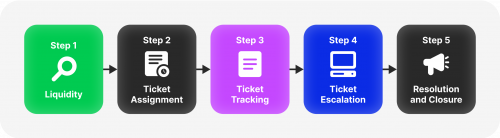
Customers or users use a ticketing system to submit their inquiries or requests through various channels such as email, web forms, or self-service portals. A unique ticket number is assigned whenever a customer submits a request. It is logged into the system, creating a detailed record of the customer’s interaction with the organisation. This record includes information such as the date and time of the request, the type of request, the customer’s contact details, and any other relevant information.
The ticketing system then uses this record to track the request’s progress and ensure that it is resolved promptly and efficiently. This helps organisations provide excellent customer service by handling every request with care and attention to detail.
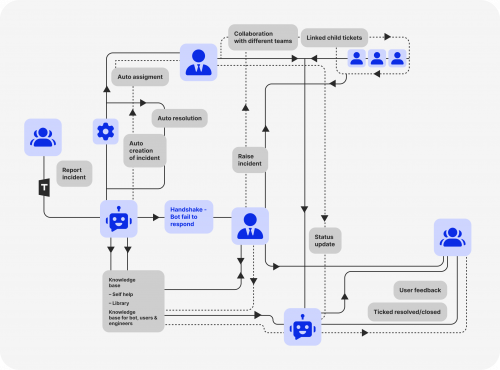
The ticketing system is an indispensable tool that streamlines the workflow for support teams by enabling them to manage and prioritise incoming tickets efficiently. With the help of this system, support agents can easily access the tickets that are assigned to them, keep track of their status, and focus on resolving them as quickly and effectively as possible. This system also empowers support teams to collaborate and communicate seamlessly, facilitating a smooth support process.
Fast Fact
The concept of ticketing systems originated from IT service management practices, where they were initially used to track and manage technical support requests and incidents.
Main Functionality of a Ticketing System
Acting as a central hub for communication between the customer helpdesk and users, the ticketing system performs several vital tasks related to the precise, fast and efficient processing and transmission of information in the context of requests for assistance in resolving specific issues.
The ticketing system streamlines communication and improves the overall customer experience by providing a smooth and hassle-free process for issue resolution.
Here are some of the key functions commonly found in ticketing systems:
Ticket Creation and Management
The ability to create, assign, and manage tickets is a fundamental feature of any online ticketing system. Users can submit tickets with relevant information about their inquiry or issue, and support agents can track, prioritise, and assign tickets for resolution.
Ticket Status Tracking
A ticketing system software allows users and support agents to track tickets’ status throughout their lifecycle. This feature provides transparency and helps users stay informed about the progress of their requests.
Ticket Prioritisation and Escalation
Tickets can be prioritised based on urgency or severity. This feature ensures that critical issues receive prompt attention and are escalated to appropriate team members if needed.
Automated Routing and Assignment
Ticketing systems often include automated routing capabilities that assign tickets to specific support agents or teams based on predefined rules or availability. This ensures efficient distribution of workload and timely responses.
Communication and Collaboration Instruments
Effective communication between end-users and support teams is crucial. Ticketing systems offer features such as threaded discussions, internal notes, and email notifications to facilitate clear and efficient communication throughout the ticket resolution process.
Knowledge Base and Self-Service Options
A good deal of maintenance ticketing systems come with a knowledge base or self-service portal where customers can find answers to frequently asked questions or troubleshoot common issues themselves. This reduces the number of incoming tickets and empowers customers to find solutions independently.
SLA Management
Service Level Agreement (SLA) management allows organisations to set response and resolution time targets for different types of tickets. The ticketing system helps monitor and enforce these SLAs to ensure timely and efficient customer support.
Reporting and Analytics
Ticketing systems often provide reporting and analytics features to help organisations gain insights into ticket volumes, response times, customer satisfaction, and other key metrics. These insights can be used to optimise support processes and identify areas for improvement.
Integration and Customisation
Integration capabilities enable ticketing systems to integrate with other tools and systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software, live chat, or social media platforms. Customisation options allow organisations to set up the ticketing system to their particular workflows and branding.
Security and Access Controls
Customer ticketing systems handle sensitive customer records, so robust security measures, such as role-based access controls, data encryption, and audit trails, are essential to protect customer data and maintain privacy.
Key Reasons for Implementing a Ticketing System
There are numerous advantages and motivations for organisations to adopt a ticketing system. Implementing such a system can streamline processes, improve efficiency, and raise the standard of customer service. By centralising ticket management, businesses can track and prioritise issues more effectively, leading to quicker resolutions and increased customer satisfaction.
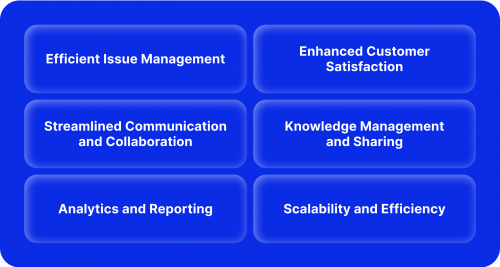
Efficient Issue Management
A ticketing system provides a structured and organised approach to managing customer concerns, issues, and requests. It ensures that every customer interaction is captured as a ticket, preventing issues from falling through the cracks or being overlooked. This systematic process improves the efficiency of issue resolution and helps support teams stay on top of customer needs.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Businesses can improve the overall customer experience and satisfaction by implementing a ticketing system. Tickets can be tracked, prioritised, and assigned to appropriate support agents based on their expertise and availability. This enables faster response times, effective communication, and timely resolution of customer issues.
Customers appreciate the visibility and transparency offered by the ticketing system, as they can easily track the progress of their requests and receive updates.
Streamlined Communication and Collaboration
An automated ticketing system serves as a centralised platform for communication and collaboration between end-users and support teams. It enables smooth information exchange, as users can submit tickets with all relevant details, and support agents can ask clarifying questions or provide updates within the ticket.
This eliminates the need for back-and-forth emails or phone calls, streamlines communication, and ensures that all relevant parties have access to the same information.
Knowledge Management and Sharing
Ticketing systems often include knowledge management features, allowing support agents to document solutions, best practices, and frequently asked questions. These resources can be easily accessed by both new and experienced team members, facilitating knowledge sharing and reducing the learning curve for newcomers. This leads to consistent and accurate responses to customer inquiries and helps build a comprehensive knowledge base over time.
Analytics and Reporting
Many ticketing systems provide analytics and reporting capabilities that offer important insights into support operations. Businesses can track metrics such as ticket volumes, response times, resolution rates, and customer satisfaction. These insights help pinpoint areas for improvement, measure team performance, and make data-driven decisions to optimise support processes and resource allocation.
Scalability and Efficiency
As businesses grow, managing customer support manually or through ad-hoc methods becomes increasingly challenging and inefficient. An internal ticketing system provides a scalable solution that can handle a high volume of customer inquiries. It streamlines workflows, automates repetitive tasks, and ensures that support agents can efficiently manage and prioritise tickets, resulting in improved productivity and resource utilisation.
Implementing a Ticketing System: A Step-by-Step Guide
The realities of modern business space stipulate the presence in each company of different kinds of systems and solutions that allow to efficiently and quickly carry out various operations within the process of interaction with customers, one of which is a powerful IT support ticketing system, the creation and implementation of which plays a paramount role in matters relating to the prompt and quality solution of issues and complex situations associated with the use of products and services of the company.

To implement a functional personal ticketing system, there is an algorithm that includes a sequence of steps or important aspects that need to be considered.
1. Identify Requirements and Objectives
Start by clearly defining your organisation’s requirements and objectives for implementing a ticketing system. Consider factors such as the volume of customer inquiries, desired response times, collaboration needs, reporting requirements, and integration with existing systems.
2. Research and Select a Ticketing System
Conduct thorough research to identify ticketing system options that align with your requirements. Evaluate factors such as features, scalability, ease of use, customisation options, and vendor reputation. Consider whether an on-premises or cloud-based solution is more suitable for your organisation. Select a ticketing system that best fits your needs and budget.
3. Plan and Prepare for Implementation
Develop a comprehensive implementation plan that outlines key milestones, timelines, resource allocation, and potential challenges. Identify a dedicated project team responsible for implementation and ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge. Prepare your existing customer assistance team for the transition by providing training and support.
4. Set Up Ticketing System Configuration
Work closely with your ticketing system vendor to configure the system according to your organisation’s requirements. Define ticket categories, escalation rules, priority levels, and any custom fields needed to capture relevant information. Set up user roles and permissions to ensure appropriate access levels for support agents and end-users.
5. Data Migration
If you are transitioning from an existing system, plan and execute the migration of your existing ticket data to the new system. Consult with your ticketing system vendor to ensure a smooth and accurate data transfer. Validate the migrated data to ensure integrity and accuracy.
6. Integrate with Existing Systems
If necessary, integrate the ticketing system with your existing system, such as CRM, knowledge base, or communication tools. This integration enables seamless data flow and improves the overall efficiency of your support processes.
7. Customise and Branding
Customise the ticketing software to align with your organisation’s branding and visual identity. Configure email templates, notifications, and customer-facing interfaces to provide a consistent and branded experience.
8. Test and Quality Assurance
Thoroughly test the ticketing system before deploying it to your live environment. Conduct functional testing, user acceptance testing, and performance testing to ensure the system operates as expected. Identify and resolve any issues or bugs before moving forward.
9. Training and Onboarding
Provide comprehensive training sessions to your support agents and other relevant stakeholders. Familiarise them with the ticketing system’s features, functionality, and best practices for using the system effectively. Offer ongoing support and resources to ensure a smooth onboarding process.
10. Rollout and Continuous Improvement
Gradually roll out the ticketing platform to your client support team and start capturing customer inquiries through the system. Monitor the system performance, gather feedback from users, and make necessary adjustments or improvements based on the feedback received. Continually evaluate and optimise your ticketing system to meet evolving needs and heighten end-user satisfaction.
Concluding Remarks
The ticketing system is an indispensable multifunctional tool in any company, providing simplicity, convenience, and efficiency in interacting with customers, as well as optimising the process of dealing with their questions and problems arising in the process of cooperation.
By implementing such a system into the infrastructure, businesses can automate routine tasks and avoid confusion and errors in organising and prioritising customer issues, which ultimately increases the company’s all-around productivity.
FAQ
What is a support ticketing system?
A customer support ticket system is vital in facilitating interpersonal interaction between clients and customer assistance agents. It simultaneously enables them to submit their inquiries and issues through support tickets, which are then allocated to the appropriate teams for resolution.
What programming languages and technologies are typically used to create a ticketing system?
Regularly used languages include PHP, Python, Ruby, Java, or NET. Frameworks like Laravel, Django, Ruby on Rails, or ASP.NET can be used to expedite development. Database technologies like MySQL or PostgreSQL are often used to store ticket data.
What are the essential features to include in a ticketing system?
Essential features of a ticketing system include ticket creation and tracking, ticket assignment and prioritisation, communication and collaboration capabilities, knowledge base integration, reporting and analytics, and user management.
Is it necessary to have a database for a ticketing system?
Yes, a database is essential for storing and managing ticket data. It lets you store customer records, ticket details, agent assignments, ticket statuses, and communication history. A database allows efficient querying, searching, and reporting on ticket data.
How can I ensure scalability and performance in a ticketing system?
Design the system with a modular and scalable architecture to ensure scalability and performance. Implement caching mechanisms to optimise performance and use load-balancing techniques for handling increased traffic.


