Share
0
/5
(
0
)
The reality of modern Forex trading is more than exciting, but for newcomers, dealing with the complexities of brokers can be terrifying. Recognising the diverse types of Forex brokers available is crucial for making a knowledgeable judgement about who will handle your hard-earned capital.
This comprehensive guide explores the various broker options, their functionalities, and how they can impact your trading experience.
Key Takeaways
DD brokers act as counterparties in trades, while Non-Dealing Desk brokers connect traders directly to the interbank market.
STP brokers route orders to liquidity providers, whereas ECN brokers allow direct exchange among traders in a network.
Forex brokers make money through spreads, commissions, and other fees.
Understanding the differences between broker types helps in selecting the best fit for your trading needs.
The Essence of Forex Brokers

The foreign exchange market, well-known as Forex, is the world's largest financial market, facilitating trillions of dollars in daily currency trades. Individual traders participate in this market through Forex brokers who act as intermediaries, bridging the gap between retail traders and the vast interbank network. They provide platforms for traders to access the Forex market, offering tools, analysis, and support. Let's outline brokers' duties in detail:
Admission to Trading Platforms
Forex brokers provide the technological infrastructure for trading, including platforms where traders can analyse market data, execute trades, and manage their accounts. They are responsible for executing buy and sell orders placed by traders on their platforms. They facilitate various order types, such as market orders, limit orders, and stop-loss orders.
Market Access
Brokers offer access to a range of currency pairs, from major pairs like EUR/USD to exotic pairs involving less commonly traded currencies. Some brokers also offer trading in commodities, indices, and cryptocurrencies, allowing traders to participate in the global Forex market.
Leverage
They often provide leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with less capital. They also manage margin requirements to mitigate risk. They offer tools such as stop-loss orders to help traders manage risk.
Liquidity Providers
Brokers play a crucial role in ensuring there is enough liquidity in the market, which is essential for the smooth execution of trades. Some brokers act as market makers, providing liquidity by taking the opposite side of a trade when there is no immediate match.
Assistance in Education
Many brokers provide tools for technical and fundamental analysis, including charts, indicators, and economic calendars. They often offer educational materials, webinars, and tutorials to help traders improve their skills. They also offer training programs and demo accounts for beginners to practice trading without financial risk.
Adherence to Regulations
Reputable brokers operate under the supervision of regulatory authorities to ensure compliance with financial laws and the protection of traders. They are responsible for maintaining transparency in their operations and ensuring the security of traders' funds and personal information.
24-hour Assistance
Brokers provide customer support to assist traders with technical issues, account management, and trading inquiries. Since the Forex market operates 24 hours a day, many brokers offer around-the-clock support.
[aa quote-global]
Fast Fact
Sucden Financial, established in 1973, is one of the longest-standing forex brokers in the market. With over 50 years of service, the company has a rich history. However, their website was not launched until 2008.
[/aa]
Main Types of Forex Brokers

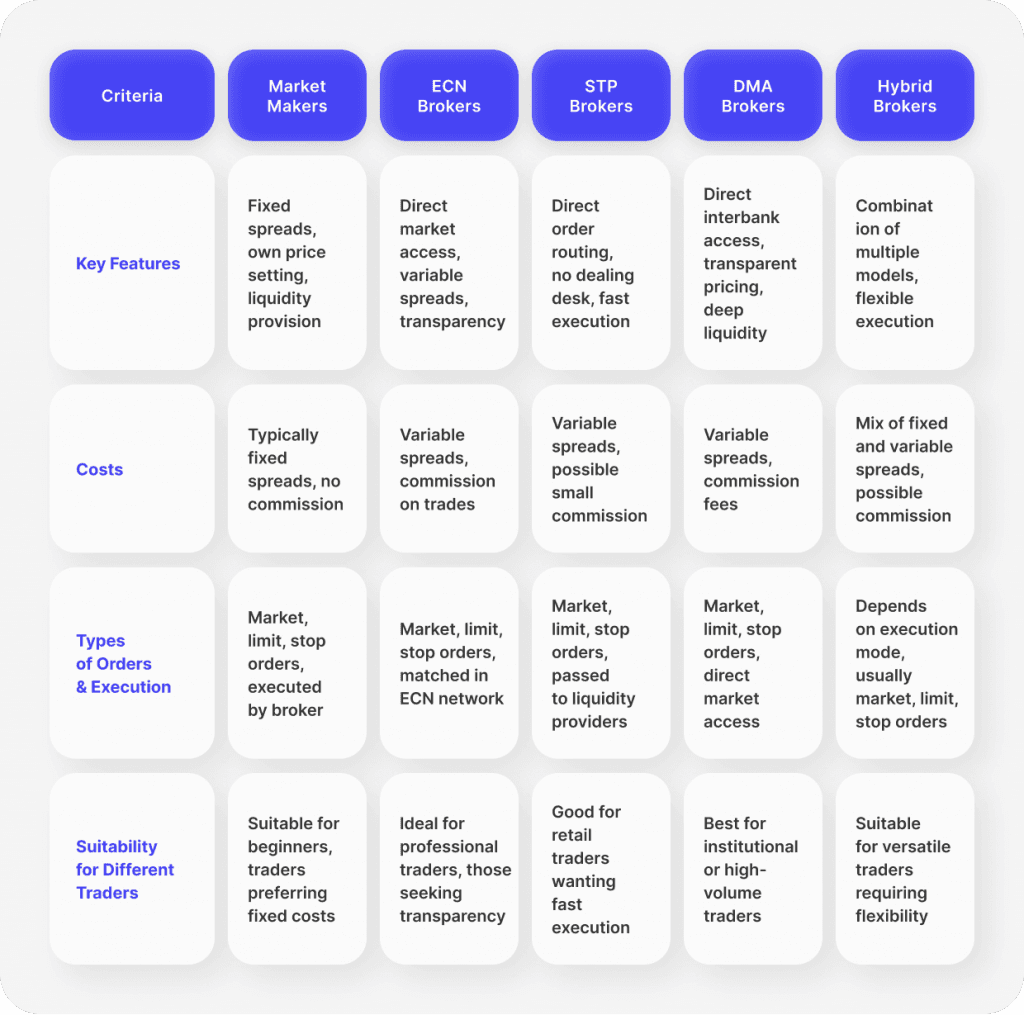
There are different types of brokers in Forex, each offering distinct trading environments and features. Understanding these categories helps traders select a broker that best suits their trading style and objectives. The main types of Forex brokers include:
Market Makers (Dealing Desk)
Non-Dealing Desk (NDD) Brokers
Electronic Communication Network (ECN) Brokers
Straight Through Processing (STP) Brokers
Direct Market Access (DMA) Brokers
Hybrid Brokers
Let's explore the difference between Forex brokers.
Dealing Desk (DD) Brokers: Market Makers with Their Own Skin in the Game
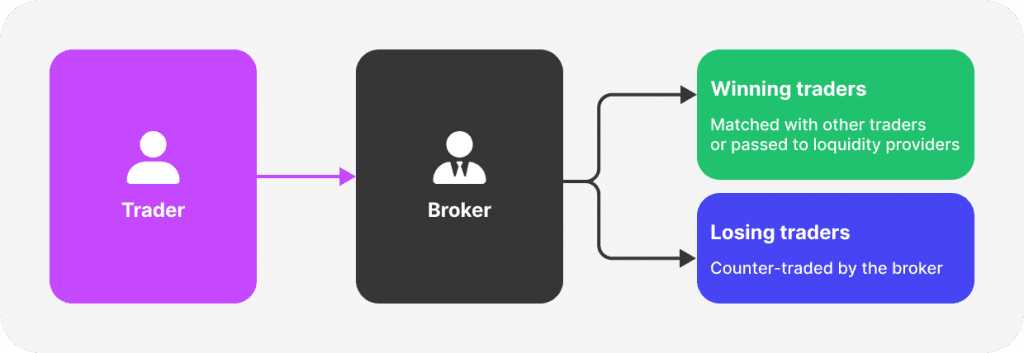
Dealing Desk brokers, also known as Market Makers, play a pivotal role in the Forex brokerage business by providing liquidity to their clients. They are called market makers because they "make the market" for their clients by setting bids, asking prices, and filling orders internally.
How Do Dealing Desk Brokers Operate?
Dealing Desk brokers take the opposite side of a client's trade, creating a counterparty risk. For instance, if a client buys a currency pair, the broker will sell it to them. This model allows brokers to profit from spreads - the difference between the buying (bid) and selling (ask) prices.
How Do DD Brokers Make Money?
Spreads: The difference between the bid and ask price is the primary source of income for DD brokers. They widen the spread to generate profit, regardless of whether your trade succeeds or fails.
Commissions: Some DD brokers may charge additional commissions on top of the spread.
Pros
DD brokers generally guarantee order execution, ensuring your trades are filled at the quoted price, even during volatile market conditions.
DD brokers typically offer fixed spreads, providing a degree of predictability for your trading costs.
Typically, DDs earn from the spread and do not charge additional commissions.
Many DD brokers cater to beginner traders, offering user-friendly trading platforms with educational resources. The availability of micro and mini accounts is beneficial for beginners.
Cons
As DD brokers profit from client losses, there can be a potential conflict of interest. Their interests may not always align with yours.
There is a risk of price manipulation, where the broker might alter prices to trigger stop losses or margin calls.
Trading against a dealer means less transparency compared to trading on a public exchange or network. Price quotes from DD brokers may not always reflect true market conditions.
Some DD brokers may restrict the types of orders you can place, limiting your trading strategies.
Non-Dealing Desk (NDD) Brokers: Facilitators Connecting You to the Market

Non-dealing desk (NDD) brokers do not take the opposite side of a client's trade. Instead, they connect traders directly to the interbank market, facilitating trades through liquidity providers. This can be through subcategories of NDD Brokers:
Straight Through Processing (STP): STP brokers route client orders directly to their liquidity providers without any intervention. They offer variable spreads, which are typically lower during times of high liquidity.
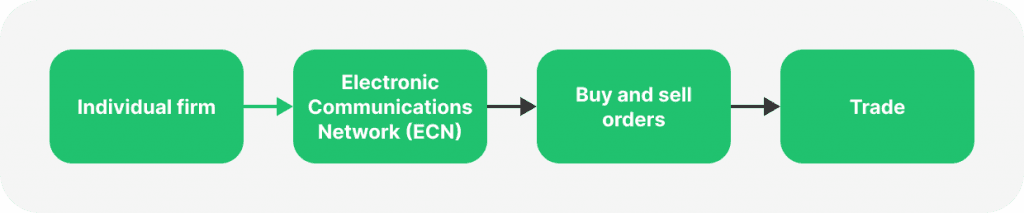
Electronic Communication Network (ECN): ECN brokers facilitate a trading environment where multiple participants, including banks, hedge funds, and other traders, can place bids and offers. ECN brokers provide a platform where traders can interact directly with each other, offering the best available bid and ask prices from the network. This model creates a transparent trading environment with low spreads.
How NDD Brokers Make Money?
Commissions: NDD brokers primarily generate revenue through commissions charged per trade. The commission structure can be fixed or variable, depending on the broker.
Spreads: NDD brokers may also earn income from the spread, but the spreads are generally tighter compared to DD brokers due to the higher level of market competition.
Pros
NDD brokers offer more transparent pricing as quotes are closer to real-time market prices.
The competitive nature of ECNs and STP networks can result in tighter spreads for traders.
NDD brokers often allow for a broader range of order types, providing more control over your trading strategies.
Cons
Spreads with NDD brokers can be variable, depending on market liquidity. This can make it challenging to predict trading costs precisely.
During periods of low liquidity, your orders may not be filled at your desired price or may be rejected entirely.
Some NDD brokers may have higher minimum deposit requirements than DD brokers.
STP vs ECN: Understanding the Differences
As mentioned above, both STP and ECN brokers are types of Non-Dealing Desk brokers, but they operate differently.
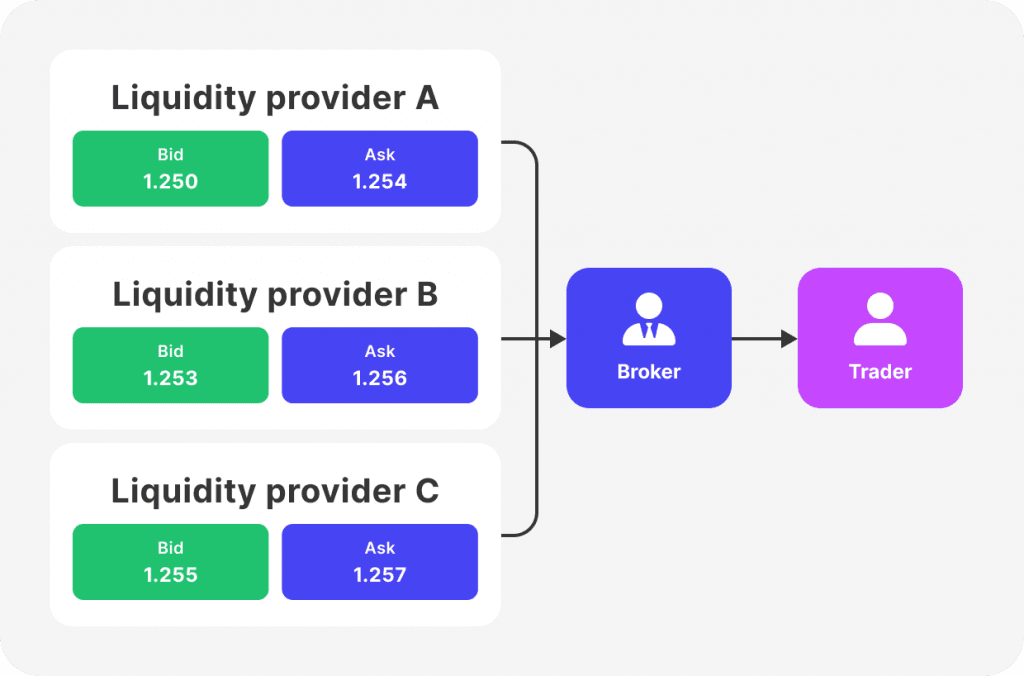
STP brokers route client orders directly to liquidity providers (such as banks or other brokers) without dealing desk intervention. Orders are processed and executed automatically through a network of liquidity providers. The broker's role is to ensure the order is matched and filled at the best available price. This process eliminates the need for a dealing desk and provides direct access to the interbank market.
Pros
STP brokers do not manipulate prices or trade against their clients.
Orders are processed quickly, which is beneficial for high-frequency trading and scalping.
STP brokers usually offer competitive, variable spreads based on the quotes from their liquidity providers.
Cons
Spreads can widen during periods of low liquidity or high market volatility.
The quality of execution depends on the broker's network of liquidity providers, which can vary.
ECN brokers create a network where traders, including banks, hedge funds, and individual traders, can interact directly. This model provides a highly transparent trading environment. ECN brokers aggregate quotes from various participants and display the best available bid and ask prices on their platforms. They match buy and sell orders within their network, enabling direct trading without intermediaries.
Pros
Traders get direct access to the best bid and ask prices available in the market.
All orders and trades are visible on the ECN, providing full transparency.
Spreads are typically lower and vary according to market conditions.
ECN brokers do not take the opposite side of trades, eliminating conflicts of interest.
Cons
ECN brokers charge a commission per trade, which can be a significant cost.
They often require higher minimum deposits than other broker types.
The trading platforms used by ECN brokers can be complex and may require advanced knowledge to use effectively.
Direct Market Access (DMA) Brokers

DMA brokers provide clients with direct access to the interbank Forex market, allowing them to interact with deep liquidity pools. They connect traders directly to major banks and financial institutions in the interbank Forex market. Orders are placed directly into the market, ensuring that trades are executed at the best possible prices.
Pros
Traders see real market prices and can interact with the true interbank market.
Orders are executed with deep market liquidity, which can result in better price fills.
Orders are not subject to manipulation by the broker.
Cons
DMA brokers typically charge commissions on trades, which can add to trading costs.
Trading through DMA often requires larger capital due to the nature of accessing institutional-grade markets.
Using DMA brokers requires advanced knowledge and understanding of the market mechanics.
Hybrid Brokers
Hybrid brokers combine features from different types of brokers, offering a flexible trading environment that can cater to various trader needs. They may operate as Market Makers for some trades while using STP or ECN models for others, depending on factors like trade size or market conditions. They can switch between models to optimise execution.
Pros
They provide a versatile trading environment, allowing traders to benefit from different execution models based on their strategy.
Hybrids can adapt to different market conditions, providing a blend of fixed and variable spreads.
They offer a balanced approach, often minimising the disadvantages associated with pure Market Maker or ECN models.
Cons
Understanding the broker's operational model can be complex as it might change under different conditions.
There may be less transparency in how orders are executed and whether the broker is acting as a Market Maker or routing orders to the market.
In Market Maker mode, hybrids might still face conflicts of interest similar to pure Market Makers.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Forex Broker
Selecting the right broker is essential for a successful trading experience. The ideal Forex broker for you depends on your individual trading goals, experience level, and risk tolerance. Here are some factors to consider when making your decision:
Trading Style
Scalpers and day traders may benefit from the tighter spreads offered by NDD brokers. Swing traders and long-term investors may prioritise the predictability of fixed spreads from DD brokers.
Experience Level
Beginner traders may find the user-friendly platforms and educational resources offered by DD brokers appealing. More experienced traders may value the greater control and transparency provided by NDD brokers.
Risk Tolerance
Traders with a lower risk tolerance may prefer the guaranteed order execution offered by DD brokers. Those comfortable with a higher degree of risk may find the potentially tighter spreads of NDD brokers attractive.
Regulatory Environment
Ensure your chosen Forex broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority to safeguard your funds and trading activities. Check if the broker has a license from the key regulatory bodies:
United States: National Futures Association (NFA), Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
United Kingdom: Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).
European Union: Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC), German Federal Financial Supervisory Authority (BaFin).
Customer Support
Good customer support is crucial, especially for resolving issues quickly. Check the availability and quality of support services offered by the broker.
Trading Platform
Evaluate the features and functionalities offered by the broker's trading platform. Consider factors like ease of use, charting tools, and order execution speed. MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and cTrader are outstanding trading platforms.
Educational Resources
Access to educational resources can be invaluable for beginners, helping them develop their trading skills and knowledge.
Trading Costs
Compare the spreads and commissions charged by different brokers. Lower trading costs can significantly impact your overall profitability.
Final Remarks
Having a deep understanding of the different types of Forex brokers and their operations is crucial for making informed decisions in the Forex market. Whether you opt for a Dealing Desk broker with fixed spreads or a Non-Dealing Desk broker with direct market access, each type offers unique advantages and considerations. By carefully considering your trading style, experience level, and risk tolerance, you can choose a broker that aligns with your specific needs and goals.
Remember, a reputable and well-suited Forex broker can be a valuable asset in your quest for Forex trading success.
FAQ
How do I know if a broker is regulated?
A legitimate broker will prominently display their licenses and regulations on their website, usually at the bottom of every page or on a dedicated legal documents page. This information should include the regulatory agency's name and license number.
How does a Forex broker make money?
In return for executing buy or sell orders, the Forex broker will charge a commission per trade or a spread. That is how Forex brokers make their money.
Is it better to choose a broker with fixed or variable spreads?
Those who choose the fixed spread account will have a difference between Ask and Bid that is always constant over time, while those who prefer an account with variable spreads will have to deal with a floating difference that changes based on certain variables, such as market conditions at the time of trading.
Is it possible to switch brokers?
It's also important to have the right paperwork when switching brokers. You will need to fill out a transfer initiation form with the new broker, also called the receiving broker. This will ensure you not only avoid unnecessary fees but also that the process will be completed on time.
Read also